New Podcast: “Crafting A Character: Brutus.”













Since Easter and Passover are coming up, (and we are already in the middle of Rhamadan), I thought I’d examine Shakespeare’s depiction of other worlds both celestial and infernal. As the quote above says, philosophers and poets often wonder what greets us in the hereafter, so let me be your guide through Shakespeare’s poetic renderings of heaven and he’ll, accompanied by some gorgeous artwork from HC Selous, William Blake, and others.
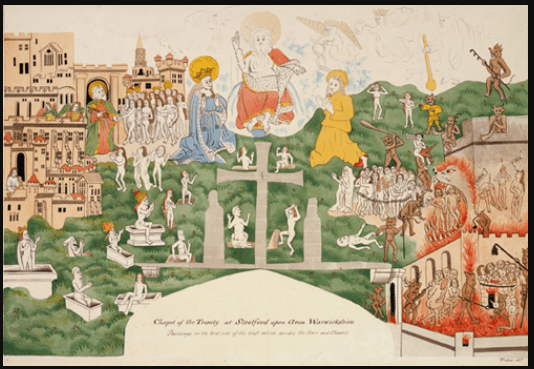
Shakespeare was no doubt interested in religion. He quotes from and alludes to the Bible many times in his plays. More importantly, he lived in a time when the national religion changed three times in just 4 years! When Henry VIII changed England to a protestant country, the religious identity of England completely changed:
This change was not just felt in monasteries, but in all English churches. King Henry decreed that certain Catholic traditions like Purgatory, indulgences, and praying to saints were idolatrous, and were therefore banned in the Church of England. So, when Shakespeare’s father was called to destroy the “idolatrous” images of the Last Judgement in the Guild Chapel of Stratford’s Holy Trinity Church, he had no choice but to comply. If you click on the link below, you can see a detailed description of the images that Shakespeare no doubt knew well in his family’s church, until his father was forced to literally whitewash them.
Like the images on the Stratford Guild chapel, the ideas of Catholic England didn’t disappear, they were merely hidden from view. Shakespeare refers to these Catholic ideas many times in his plays, especially in Hamlet, a play where a young scholar, who goes to the same school as Martin Luther, is wrestling with the idea of whether the ghost he has seen is a real ghost from purgatory, or a demon from hell, (as protestant churches preached in Shakespeare’s life).

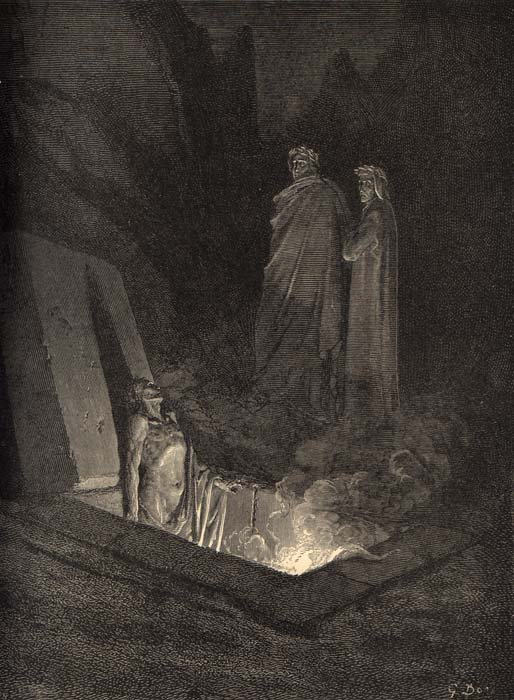
I’ve written before that the ghost of Hamlet’s father teases us with the possibility that he might be a soul in purgatory, the Catholic afterlife realm for those not evil enough for Hell, nor good enough for Heaven. At the height of their powers, monks and bishops sold prayers called indulgences that supposedly allowed a soul’s loved ones to buy them time out of purgatory, thus making them able to ascend to Heaven quicker. The image above is an illustration from Purgatorio, part of Dante’s Divine Comedy, where he visits the soul of
Buonconte da Montefeltro, who is languishing because he doesn’t yet have the strength to get out of purgatory and enter Heaven.
Of course, the Tudor monarchs Henry VIII and Elizabeth I abolished indulgences and proclaimed that purgatory itself didn’t exist, but ideas can’t die, and I feel that Shakespeare was at least inspired by the notion of purgatory, even if he didn’t believe in it himself.

(Horatio) Hamlet, Act I, Scene i.
As a young boy, William Shakespeare was entertained by medieval Mystery plays; amateur theater pieces performed by local artisans that dramatized great stories from the Bible. We know this because he refers to many of the characters in these mystery plays in his own work, especially the villains. King Herod is mentioned in Hamlet and many other plays in and many of Shakespeare’s villains seem to be inspired by the biblical Lucifer, as portrayed in Medieval Mystery Plays.
In this short video of the Yorkshire Mystery play “The Rise and Fall of Lucifer,” we see God (voiced by Sir Patrick Stewart), creating Lucifer as a beautiful angel, who then, dissatisfied with his place in God’s kingdom, is transformed into an ugly devil. At first, Lucifer mourns losing his place in Paradise, but then finds comfort by becomming God’s great antagonist.
Compare this character arc with Shakespeare’s Richard of Gloucester, who also blames his unhappiness on God, (since he feels his disability and deformity are a result of God’s curse). Richard is angry with God, nature, and society, so he wages against them all to become king.
“Then since the heavens hath shaped my body so, let Hell make crook’d my mind to answer it.”
Richard of Gloucester, Henry VI, Part III, Act III, Scene i.
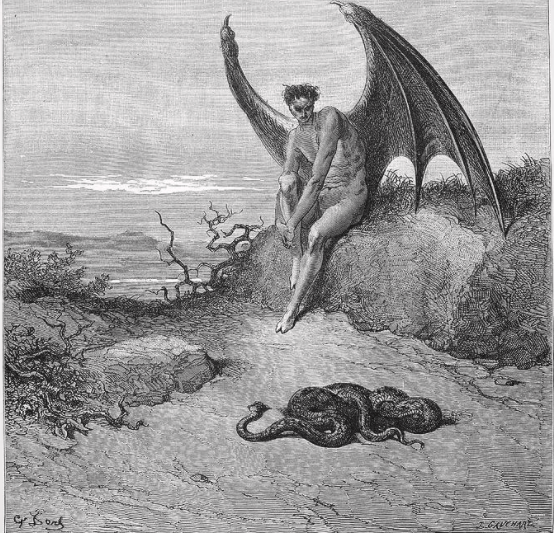


“All is not lost, the unconquerable will, and study of revenge, immortal hate, and the courage never to submit or yield.”
Lucifer― John Milton, Paradise Lost
Claudio. Ay, but to die, and go we know not where;
To lie in cold obstruction and to rot;
This sensible warm motion to become
A kneaded clod; and the delighted spirit
To bathe in fiery floods, or to reside
In thrilling region of thick-ribbed ice;
To be imprison’d in the viewless winds,
And blown with restless violence round about
The pendent world; or to be worse than worst
Of those that lawless and incertain thought Imagine howling: ’tis too horrible!
—Measure For Measure, Act III, Scene i

“Methought I crossed the meloncholy flood with that grim ferryman the poets write of, into the kingdom of perpetual night.”
— Richard III, Act I, Scene iv.

The heavens themselves, the planets and this centre
Observe degree, priority and place,
Insisture, course, proportion, season, form,
Office and custom, in all line of order;
And therefore is the glorious planet Sol
In noble eminence enthroned and sphered
Amidst the other; whose medicinable eye
Corrects the ill aspects of planets evil,
And posts, like the commandment of a king,
Sans cheque to good and bad: but when the planets
In evil mixture to disorder wander,
What plagues and what portents! what mutiny!
What raging of the sea! shaking of earth! Commotion in the winds! frights, changes, horrors,
Divert and crack, rend and deracinate
The unity and married calm of states
Quite from their fixure! O, when degree is shaked,
Which is the ladder to all high designs,
Then enterprise is sick! - Troilus and Cressida, Act I, Scene iii.
https://folgerpedia.folger.edu/Idolatry:_Icons_and_Iconoclasm



The goal of this class is to learn about both Shakespeare and the Elizabethan period through the lens of Christmas. I will begin by asking the class "What traditions do you think of when you think of Christmas? We will then contrast the traditions of Christmas from the 17th century and now, including a brief period when Christmas itself was illegal.
Once I have contextualized this period, we will then go through the plot, characters, and themes of Shakespeare’s most famous Christmas play- “Twelfth Night.”
The class will include videos, multimedia presentations, virtual tours, interactive quizzes, and online activities. The students will play games inspired by real Elizabethan Christmas traditions, get some festive recipes, and learn what it was like to be an actor in Shakespeare's company, when they performed "Twelfth Night" and other plays before Queen Elizabeth and King James.

This video is part of my Outschool course “Macbeth: An Immersive Horror Experience.” I use it to explain the plot of the play before playing a game and an escape room to test the student’s knowledge. Let me know in the comments what you think of it, and if you like it, please consider signing up for the course on Outschool.com

Happy St. Patrick’s Day! The Emerald Isle has long been a source of illumination for poet’s pens and Shakespeare was no exception. The Bard of Avon is indebted to Mother Ireland not only for the inspiration he took, but sadly for the pain he gave her back.
None of Shakespeare’s plays are set in Ireland, but he freely adapted elements from Irish folklore. English poet Edmund Spencer visited Ireland in the 1590s and adapted the folklore he picked up into his opera The Fairy Queen, which Shakespeare adapted into A Midsummer Night’s Dream
The Irish created and continue to tell many of the fairy legends and stories that we retell and adapt today. If you go to Lullymore park in Ireland, you can see a place that is essentially a “Fairy preserve.”

The old stories tell that Fairies are magical creatures who live in hollow places in the earth. Some are benevolent and help give rain and pleasant weather to the Earth, Like the king and Queen of the fairies, Oberon and Titania:
Titania in this speech shows great concern for nature, humanity, and the planet. She believes it is the responsibility of fairies, particularly herself and her husband Oberon, to control the elements and keep humans and fairies safe. Some fairies, however, are cruel and enjoy playing tricks on mortals, just like Puck in A Midsummer Night’s Dream, or Queen Mab in Romeo and Juliet.
.
This is a short analysis I created of the tricks Puck plays on people in A Midsummer Night’s Dream, as part of my acting course on Ouschool.com. Note the different ways Puck is portrayed in photos as a satyr, a rotund elf, and sometimes as an almost- demon like figure.
When Shakespeare is racially insensitive towards people of color, the cringe-worthy writing is mercifully few and far between. With the exception of Aaron the Moor and Don Armada, there are only a few sporadic derogatory references to non-White Anglo-Saxon Protestants. Sadly though, Shakespeare might have permanently harmed the Irish through his character the Irish captain Macmorris in Henry the Fifth, his only Irish character.
According to The Irish Times, there is a longstanding stereotype that still exists in the British Isles that Irish people are violent, short-tempered, and essentially savages and Shakespeare might have invented this stereotype (or at least popularized it) when he wrote this scene from Henry the Fifth, Act III, Scene ii:
FLUELLEN
To the mines! tell you the duke, it is not so good
to come to the mines; for, look you, the mines is
not according to the disciplines of the war: the
concavities of it is not sufficient; for, look you,
the athversary, you may discuss unto the duke, look
you, is digt himself four yard under the
countermines: by Cheshu, I think a' will plough up
all, if there is not better directions.
GOWER
The Duke of Gloucester, to whom the order of the
siege is given, is altogether directed by an
Irishman, a very valiant gentleman, i' faith.
FLUELLEN
It is Captain Macmorris, is it not?
GOWER
I think it be.
FLUELLEN
By Cheshu, he is an ass, as in the world: I will
verify as much in his beard: be has no more
directions in the true disciplines of the wars, look
you, of the Roman disciplines, than is a puppy-dog.
Enter MACMORRIS and Captain JAMY
GOWER
Here a' comes; and the Scots captain, Captain Jamy, with him.
FLUELLEN
Captain Jamy is a marvellous falourous gentleman,
that is certain; and of great expedition and
knowledge in th' aunchient wars, upon my particular
knowledge of his directions: by Cheshu, he will
maintain his argument as well as any military man in
the world, in the disciplines of the pristine wars
of the Romans.
JAMY
I say gud-day, Captain Fluellen.
FLUELLEN
God-den to your worship, good Captain James.
GOWER
How now, Captain Macmorris! have you quit the
mines? have the pioneers given o'er?
MACMORRIS
By Chrish, la! tish ill done: the work ish give
over, the trompet sound the retreat. By my hand, I
swear, and my father's soul, the work ish ill done;
it ish give over: I would have blowed up the town, so
Chrish save me, la! in an hour: O, tish ill done,
tish ill done; by my hand, tish ill done!
FLUELLEN
Captain Macmorris, I beseech you now, will you
voutsafe me, look you, a few disputations with you,
as partly touching or concerning the disciplines of
the war, the Roman wars, in the way of argument,
look you, and friendly communication; partly to
satisfy my opinion, and partly for the satisfaction,
look you, of my mind, as touching the direction of
the military discipline; that is the point.
JAMY
It sall be vary gud, gud feith, gud captains bath:
and I sall quit you with gud leve, as I may pick
occasion; that sall I, marry.
MACMORRIS
It is no time to discourse, so Chrish save me: the
day is hot, and the weather, and the wars, and the
king, and the dukes: it is no time to discourse. The
town is beseeched, and the trumpet call us to the
breach; and we talk, and, be Chrish, do nothing:
'tis shame for us all: so God sa' me, 'tis shame to
stand still; it is shame, by my hand: and there is
throats to be cut, and works to be done; and there
ish nothing done, so Chrish sa' me, la!
JAMY
By the mess, ere theise eyes of mine take themselves
to slomber, ay'll de gud service, or ay'll lig i'
the grund for it; ay, or go to death; and ay'll pay
't as valourously as I may, that sall I suerly do,
that is the breff and the long. Marry, I wad full
fain hear some question 'tween you tway.
FLUELLEN
Captain Macmorris, I think, look you, under your
correction, there is not many of your nation--
MACMORRIS
Of my nation! What ish my nation? Ish a villain,
and a bastard, and a knave, and a rascal. What ish
my nation? Who talks of my nation?
FLUELLEN
Look you, if you take the matter otherwise than is
meant, Captain Macmorris, peradventure I shall think
you do not use me with that affability as in
discretion you ought to use me, look you: being as
good a man as yourself, both in the disciplines of
war, and in the derivation of my birth, and in
other particularities.
MACMORRIS
I do not know you so good a man as myself: so
Chrish save me, I will cut off your head.
GOWER
Gentlemen both, you will mistake each other.
JAMY
A! that's a foul fault.
A parley sounded
GOWER
The town sounds a parley.
FLUELLEN
Captain Macmorris, when there is more better
opportunity to be required, look you, I will be so
bold as to tell you I know the disciplines of war;
and there is an end.
Exeunt
The mayor and all his brethren in best sort,
Like to the senators of the antique Rome,
With the plebeians swarming at their heels,
Go forth and fetch their conquering Caesar in:
As, by a lower but loving likelihood,
Were now the general of our gracious empress,
As in good time he may, from Ireland coming,
Bringing rebellion broached on his sword,
Henry V, Act V Chorus
James Shapiro in his excellent book, A Year In The Life Of William Shakespeare, 1599, posits that contemporary affairs in Ireland might have inspired some of Shakespeare’s greatest plays in including Richard II, Henry V, and Julius Caesar. In 1594 the Earl of Tyrone began a rebellion in Ireland against the English, and in 1599, Queen Elizabeth dispatched the ambitious and chivalrous Earl of Essex to quell it. As you can see in the quote above, Shakespeare mentions Essex’s fight in his play of Henry V, which probably premiered at around the same time Essex was in Ireland.
The audience may have been watching Henry conquer France, but many would have been thinking about Elizabeth’s struggle to conquer Ireland.
BBC Radio 4 Extra – Shakespeare’s Restless World, Ireland: Failures in the Present – Transcript – Shakespeare’s Restless World – Programme 7
Though King Henry successfully conquered and united England and France, Essex failed spectacularly, and Elizabeth was deeply embarrassed by the whole scenario. She was also deeply alarmed by the popularity of Shakespeare’s tragedy Richard II, which shows onstage the deposing and killing of a king who had no children and failed to quell a rebellion in Ireland.
Elizabeth was worried about her subjects but she was also very worried about Essex overseas. Everyone, (including Shakespeare), remembered that 2,000 years ago, Julius Caesar went from him the Senate’s Consul General to dictator by amassing an army, then threatening to invade Rome under the pretense of helping to quell a foreign invasion. Caesar made his name by subjugating tribes in Gaul (modern-day France), and the Senate was worried that he would come home and use his army for a military coup. Look at the expressions on the faces of Cicero and Brutus when they see Caesar coming home in triumph in this scene from the HBO series Rome.
Elizabeth repeatedly attempted to curb Essex’s power while he was fighting in Ireland; she refused to give the Earl more troops for fear that he might be staging a potential coup. Her fears would later be proven right when in 1602, Essex attempted to head a rebellion and take the Crown for himself, but not before one of Essex’s friends commissioned Shakespeare’s company to portray the deposing and killing of King Richard II. Essex was trying to turn himself from a failed Henry V to a victorious Henry IV, and his queen into Richard II.


Shakespeare might have been inspired to write Julius Caesar after being an unwitting pawn in the political drama between Essex and the queen, and might have even created the character of Cinna the Poet as an analog for Shakespeare himself. In the play, Cinna the poet is mistaken for one of the conspirators by an angry mob and is murdered in the street. Perhaps Shakespeare created Cinna the Poet as a way of coping with the fear he must have had that people might mistake him for a radical, after his play Richard II briefly made him a walking target for those opposed to Essex’s rebellion. In any case, Julius Caesar eloquently documents the kind of anxiety of not knowing who could be trusted when it comes to politics, whether it be a populist warrior like Julius Caesar or Essex, or the Queen, privy council, or indeed Roman senate, and the whole thing started from a failed attempt to quell a rebellion in Ireland.
In summation, even though Shakespeare sets no plays in Ireland, Irish history and Irish culture are everywhere in his plays. England and Ireland are I are indeed separate islands but the cultural exchange between England and Ireland has inspired Shakespeare and many other great writers for centuries. After all Shakespeare’s most famous honorific, ‘the Bard of Avon’ comes from an ancient Irish tradition of semi-mystical poets, who in Irish folklore, were able to see the future and glimpse worlds that are unseen to ordinary mortals. What Shakespeare really felt about Ireland we don’t know but we do him but he does owe the Irish people a lot of thanks, and on this Saint Patrick’s day, I honor their contribution to him and to him all the world
References:
Shapiro, James. A Year In the Life Of William Shakespeare, 1599. Chapter 6: Things Dying and Things Reborn.


Let me begin by admitting that this post was harder to write than my Christmas post because pre Christian traditions are harder to pin down. In addition, to give you my standard disclaimer, I don’t believe it’s really possible to definitively know how or if Shakespeare celebrated Halloween, but since the history of Halloween is long and fascinating, and since Shakespeare’s plays influenced that history, I feel it’s worth exploring.
Part I: Origins of Halloween
Almost every culture on Earth has a middle fall celebration that calls to mind the bounty of the harvest, and the inevitable approach of winter. Most of our Halloween traditions are based on the ancient European festival of Samhuin.
What is Samhuin?
Over 2,000 years ago, the Celts inhabited much of the British Isles. They believed in many gods and spirits that controlled nature and the seasons. To thank the gods for the harvest the Celts gave them offerings like apples, and threw parties to celebrate the gods’ bounty.
When the Romans conquered the Celts, they co-opted some of their religious practices. For instance the tradition of giving apples as offerings to the Roman goddess Pomona. This tradition of course, evolved into our modern Halloween tradition of bobbing for apples. Honoring the harvest also went hand in hand with darker traditions; ones inspired by fear of death, decay, and evil spirits.
With the Sun dying and the Earth growing cold in late October, cultures like the Celts and the Romans feared that evil fairies and ghosts could cross over into our world. In particular the Celts believed that around the night of October 31st, the veil between the living and the dead was the thinnest.
Samhuinn was a liminal time between our world and the Otherworld. It’s a night when the souls of dead loved ones as well as spirits and fairies – the aos sí in Irish mythology and aes sídhe or sìth in Scottish mythology – could come through to visit. Deceased family members were honoured with seats at the evening feast, and offerings of milk and baked goods were left at the front door for the Fairies.
At some point people decided to dress up as the spirits to ward them off, and this evolved into our modern day trick or treating.
These traditions did not die once England became Christian, (after it was conquered by the Romans), they simply translated into a different form. Halloween actually translates as “All Hallows Eve,” a Catholic celebration of of dressing up as pagan spirits and giving offerings of the harvest to honor Catholic saints as well as departed love ones.
Part II: What might Shakespeare have Done on Halloween?
Although Shakespeare never directly mentions Halloween, he lived in a world that kept many of these folk traditions alive. Shakespeare was the grandson of a farmer and his father was a devout Catholic, so he probably was brought up in these ancient Halloween traditions. He probably would have attended some kind of harvest festival to celebrate the bounty of the summer, and might have put food out for his departed family members.
Samhain is still heralded by the baking of kornigou, cakes baked in the shape of antlers to commemorate the god of winter shedding his ‘cuckold’ horns as he returns to his kingdom in the otherworld. On the Isle of Man in the Irish sea, the Manx celebrate Hop-tu-Naa, which is a celebration of the original New Year’s Eve and children dress as scary beings, carry turnips and go from home to home asking for sweets or money.
Source: https://theancientweb.com/2010/10/the-origins-of-halloween-part-1/
Call me a softie but I really like the idea of Shakespeare baking treats like soul cakes for neighborhood kids or telling scary stories about a bonfire. The kornigou is more commonly known as the Soul Cake, and it’s still popular today. It’s even been immortalized in song:
You can even make it yourself: www.cardamomdaysfood.com/recipe/soul-cakes/
Another tradition was dancing around ancient Celtic burial mounds. According to tradition, these mounds were home to spirits and Fairies, and could be portals to the land of the dead. In Irish folklore, poets and storytellers had the power to pass between these two realms. Maybe Shakespeare himself visited such a mound in his youth and was inspired to write about the fairy queen Titania and the hobgoblin Robin Goodfellow. Archeologists are still learning about these ancient ruins today (source: Smithson.com)
• Theater

The most tantalizing ancient Halloween tradition is mumming, a kind of amateur theater practiced by the ancient Celts. Like modern Sunday school plays the plays were a religious ritual designed goal to honor the gods and the harvest.
Mumming, a type of folk play, was used to tell traditional Samhuinn stories about battles or the winter goddess Cailleach (meaning “old hag”), who began winter by washing her hair in the whirlpool of Corryvreck.
For a modern example of this of these traditions you can look at the Edinburgh fire festival which preserves the kind of mumming that the Celts might have done on Samhuin and Shakespeare might have seen. It’s highly ritualistic, immersive, and the characters have spooky similarities to some of Shakespeare’s plays.
To give you an idea of how mumming might have influenced Shakespeare, watch this trailer for the 2017 Edinburgh Fire Festival:
• What you can see in the trailer:
1. Keening- the wild women screaming as a way to lament, honor, and guide the dead. Characters like Constance in King John have many similar qualities.
2. The fight between the Summer King and the Winter Lord. Many Celtic stories dramatize the change of seasons from summer to winter as a battle. Even the duel between King Arthur and his young son Mordred could be seen in this context. In another interesting interpretation, Jennifer Lee Carroll in her book Haunt Me Still, interprets this mummers play as a pagan retelling of the story of Macbeth.
3. You can see brightly colored figures some designed to honor the changing of the seasons, and wild, animalistic people, presumably playing the roles of the Fairies, goblins, or other creatures that appear on Samhuin. It’s not much of a stretch to see these figures as the Fairies of Midsummer Night’s Dream, or the witches of Macbeth.
Part III: What did Shakespeare mention about Halloween?

Ghosts appear in five of Shakespeare’s plays. We see reference to all kinds of Fairies, goblins, and spirits and even a couple times people dressing up to ward off evil. In Titus Andronicus, the queen of the Goths disguises herself and her sons as spirits of revenge and go to Titus’ house to torment him, and then the old man Titus tricking them into coming to his house, where he takes his revenge.

One Shakespeare play that I think perfectly encapsulates the Halloween traditions of the English countryside is Merry Wives Of Windsor, specifically the scene in which Falstaff is tormented by a ghost story.
In the play, the fat, drunk knight Sir John Falstaff has been trying to seduce two married women, Mistress Page and Mistress Ford. Page devises a plan to scare and humiliate Falstaff, by dressing up her husband as the terrifying ghost of Herne the Hunter:
• 4.4 MISTRESS PAGE
• There is an old tale goes that Herne the hunter,
Sometime a keeper here in Windsor forest,
Doth all the winter-time, at still midnight,
Walk round about an oak, with great ragg’d horns;
And there he blasts the tree and takes the cattle
And makes milch-kine yield blood and shakes a chain
In a most hideous and dreadful manner:
You have heard of such a spirit, and well you know
The superstitious idle-headed eld
Received and did deliver to our age
This tale of Herne the hunter for a truth.

Herne the Hunter is a real medieval legend about a man who was hanged for poaching deer in Windsor park and now haunts the forest with horns on his head. Not only does Master Ford dress as Herne, The witty housewives dress the neighborhood children like Fairies and instruct them to pinch the fat knight and burn him with lit candles. Essentially this scene is a Shakespearean trick or treating moment with a ghost story to boot. Plus as Mistress Page mentioned, the ghost haunts Windsor towards the the oncoming of Winter, so it’s not entirely unlikely that it would be that this scene was originally played around the time of Halloween.

How did Shakespeare contribute?

Scholars describe Shakespeare’s mind like a magpie, taking myths, legends, history, and books to come up with his own plays. As you have seen, the ancient traditions of Halloween had a powerful effect on Shakespeare’s plays. But, did he contribute to those traditions himself? I would say yes in a big way. First of all the image of Hamlet holding a skull has inspired many other Halloween images:

David Tennant in Hamlet, RSC 2008
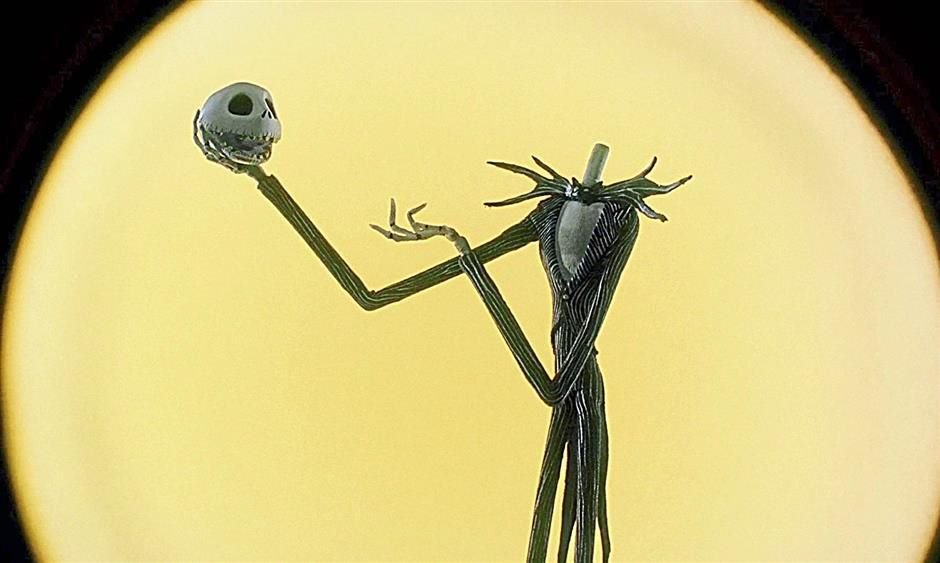

Jack Skellington in The Nightmare Before Christmas, 1993.
But I think Shakespeare’s greatest contribution to how we celebrate Halloween are centered within the witches of Macbeth.

Though Shakespeare by no means invented the concept of witchcraft, he did popularize the idea of the wicked witch, and helped form our modern view of what a witch is. The image he created in Macbeth
More than that, I would argue that the modern wicked witch would be all but silent without Shakespeare. When you think of what a witch might say, besides a series of high pitched cackling, what do you think of? Probably you think of this:

Or this:

Shakespeare’s bizarre and cryptic language helped inspire countless other interpretations of witches, and thus, a way for audiences to deal with the temptations that lurk in our hearts.




In conclusion, we don’t know how Shakespeare celebrated Halloween or even if he did to begin with; Halloween and Shakespeare’s life are both frought with mystery and legend, but one thing is dead certain; Halloween would not be the same without him. He absorbed the ancient rituals of the Celts and Romans and crafted some modern Halloween ideas and images that endure to this day.
Sources
https://www.historic-uk.com/CultureUK/Halloween/
https://www.bbc.co.uk/newsround/15169373
Thanks very much for reading! If you liked this post, please consider signing up for my new “Macbeth” online class via Outschool.com. One really fun part of the class will be an escape room where you use your knowledge of Macbeth to escape a cursed castle:


Before we continue our exploration of Shakespeare’s “Richard the Third,” I would be remiss if I didn’t spend a little time talking a little about the real Richard Plantagenet, Duke Of Gloucester and king of England from 1483-1485. I have to get this out of the way first and foremost: although “Richard III” is classified as a history play, most of the facts in it are untrue, or severely exaggerated. In this post I will try to separate the character from the man to try and make clear what Shakespeare changed from history and why.
First, a video bio I created:
The facts are these:
-He was a real English monarch who reigned 1483-1485.
– Richard was the younger brother of King Edward IV, and helped his brother take the crown away from King Henry VI, in a series of battles known as The Wars Of the Roses.
– The battles got their name because Richard’s family (the House Of York), used a white rose as its symbol, while King Henry’s faction used a red rose.
– Like Ned Stark in Game of Thrones, Richard was the undesputed “Warden Of the North,” in charge of crushing a potential Scottish invasion.
– In April of 1483, Richard’s brother King Edward IV died. As Lord Protector of England, Richard was entrusted to take care of the country, and Edward’s two sons (the new heirs to the throne). In late May, Richard arrested three lords on suspicion of treason while he guided the two princes to London. Within one month, the two princes were publicly declared illegitimate by the Archbishop, thus making Richard the new king.
– Sometime during Richard’s two year reign, Edward’s sons disappeared. Many believe they were murdered and Shakespeare’s sources named James Tyrrell and Michael Forrest as the murderers, acting under King Richard’s orders. In 1674, the skeletons of two boys believed to be the princes were discovered in the Tower Of London. The remains were interred by King Charles II. So far, nobody has confirmed if the remains belong to the princes or what happened to the young boys.
-Richard was defeated and murdered by Henry Tudor, Earl of Richmond at the Battle Of Bosworth Field on August 22, 1485. His successor founded the House Of Tudor which included Henry VIII, Mary I, Edward VI, and Queen Elizabeth I.
-in 2015, historian Phillipa Langley discovered King Richard’s remains in a parking lot in Leicester
Few contemporary sources survive from Richard’s day, so it’s unknown whether Richard did kill the princes. Even more mysterious, although he did work to depose a king, oppress the Scots, and take the throne from Edward’s kids, some sources claim Richard was actually a just and good king. In the lack of facts, Richard’s legend continues to grow
Reality check
 -After finding his skeleton, scientists discovered that Richard was not deformed, although he did have scoliosis. Thomas Moore added the hump, while Shakespeare added the withered arm.
-After finding his skeleton, scientists discovered that Richard was not deformed, although he did have scoliosis. Thomas Moore added the hump, while Shakespeare added the withered arm.
– There is no physical evidence that Richard killed the two princes, and many others wanted them dead, including Henry Tudor himself!
-Richard also probably was a good king according to some contemporary accounts, as you can see in this video with Monty Python’s Terry Jones:
Why were the facts twisted?
– Shakespeare’s main source was a history by Sir Thomas More, who was 12 at the time of Richard’s reign. More was Henry VIII’s royal chancellor, so he couldn’t afford to be nice to Richard either. More’s history set the groundwork for Shakespeare’s portrayal of Richard as a deformed monster.
The point is, people have known for centuries that Shakespeare’s Richard is no more true than the myth of Robin Hood. Even Laurence Olivier admits before his film even starts that this story has been “scorned in proof thousands of times.” Nevertheless, like Robin Hood, this story is part of the fabric of English society, and it still has value as a cautionary tale about corrupt governments, and how one man may lose his soul (and a horse) in pursuit of power and revenge.
Even today, people continue to gain power by manipulating fear, hatred, and religion, which is why we as a society need Shakespeare’s Richard. The play is so universal it was re interpreted in 2007 as “Richard III: an Arab tragedy.” Shakespeare’s Richard is so close to today’s dirty politicians that we have TV shows on both sides of the Atlantic inspired by him, (more on that later). And Richard himself is so compelling a character that centuries of great actors, cartoon characters, and even occasional rock stars have wanted to emulate him.
The lesson of the story is that a single demagogue can gain control of a corrupt system if we let him. Hitler, Saddam, Trump. It’s no accident that Olivier chose to play Richard right as the war was ending in Europe, and his popularity in that role rose exponentially after post war Britain saw the parallels between the “honey words” of Richard, which captivated England, to Hitler’s fiery rhetoric, which nearly destroyed it. The larger point through all four plays of Shakespeare’s history cycle, (not just “Richard III,”) is that greed and cruelty within one family can lead to chaos on a large scale, especially when it’s the royal family.
For more information:
Books:
Websites:
The Richard III Society: Official website of the society dedicated to preserving the memory of Richard III.
Historic UK: Short biographies of English Monarchs
Leicester Cathedral’s Richard III Page: http://kingrichardinleicester.com See pictures and read about Richard’s final resting place, and how his remains were found, and re-interred.
Westminster Abbey- The tomb of most English kings and queens for over 1,000 years:
http://www.westminster-abbey.org/our-history/royals?start_rank=1

Hi everyone,
Just wanted to let you know that I’ll be extending Romeo and Juliet for the next two weeks because it’s the start of the school year, and I still have plenty more to say about this play. So for the moment, here’s the list of posts I’ve done so far:
By the way, here’s a hilarious summary of the play from “Zounds, Alack, and By My Troth,”