Happy St. Patrick’s Day! The Emerald Isle has long been a source of illumination for poet’s pens and Shakespeare was no exception. The Bard of Avon is indebted to Mother Ireland not only for the inspiration he took, but sadly for the pain he gave her back.
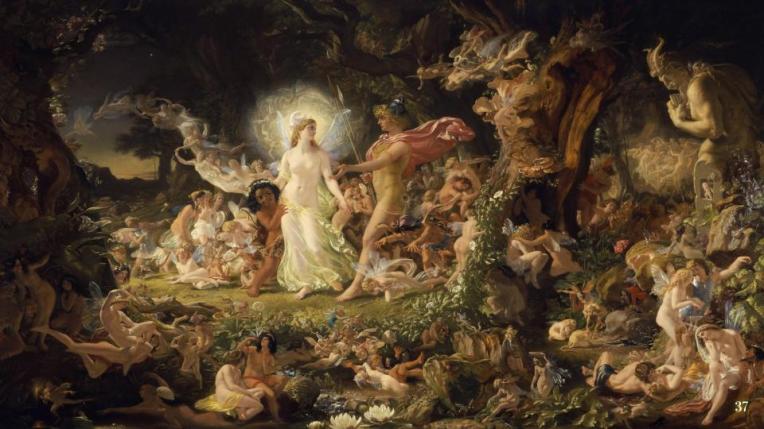
None of Shakespeare’s plays are set in Ireland, but he freely adapted elements from Irish folklore. English poet Edmund Spencer visited Ireland in the 1590s and adapted the folklore he picked up into his opera The Fairy Queen, which Shakespeare adapted into A Midsummer Night’s Dream
The Irish created and continue to tell many of the fairy legends and stories that we retell and adapt today. If you go to Lullymore park in Ireland, you can see a place that is essentially a “Fairy preserve.”

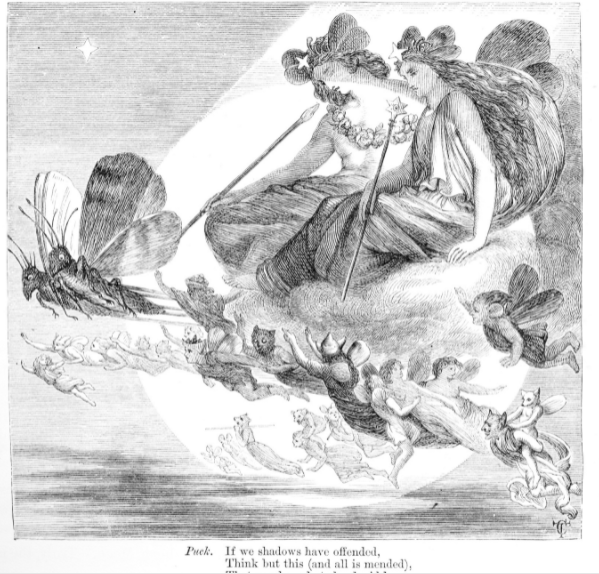
The old stories tell that Fairies are magical creatures who live in hollow places in the earth. Some are benevolent and help give rain and pleasant weather to the Earth, Like the king and Queen of the fairies, Oberon and Titania:
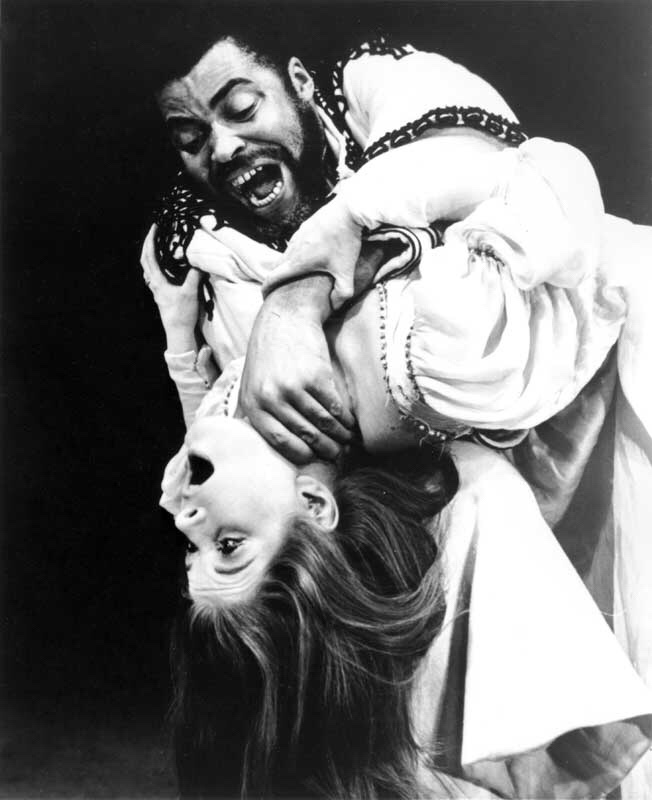
Titania in this speech shows great concern for nature, humanity, and the planet. She believes it is the responsibility of fairies, particularly herself and her husband Oberon, to control the elements and keep humans and fairies safe. Some fairies, however, are cruel and enjoy playing tricks on mortals, just like Puck in A Midsummer Night’s Dream, or Queen Mab in Romeo and Juliet.
.
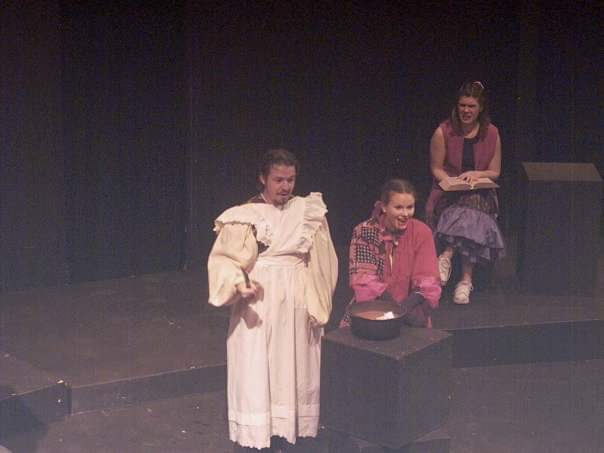
This is a short analysis I created of the tricks Puck plays on people in A Midsummer Night’s Dream, as part of my acting course on Ouschool.com. Note the different ways Puck is portrayed in photos as a satyr, a rotund elf, and sometimes as an almost- demon like figure.
Cringe-worthy Shakespeare: Shakespeare’s only Irish character, captain mcmorris in “Henry V”
When Shakespeare is racially insensitive towards people of color, the cringe-worthy writing is mercifully few and far between. With the exception of Aaron the Moor and Don Armada, there are only a few sporadic derogatory references to non-White Anglo-Saxon Protestants. Sadly though, Shakespeare might have permanently harmed the Irish through his character the Irish captain Macmorris in Henry the Fifth, his only Irish character.
According to The Irish Times, there is a longstanding stereotype that still exists in the British Isles that Irish people are violent, short-tempered, and essentially savages and Shakespeare might have invented this stereotype (or at least popularized it) when he wrote this scene from Henry the Fifth, Act III, Scene ii:
FLUELLEN
To the mines! tell you the duke, it is not so good
to come to the mines; for, look you, the mines is
not according to the disciplines of the war: the
concavities of it is not sufficient; for, look you,
the athversary, you may discuss unto the duke, look
you, is digt himself four yard under the
countermines: by Cheshu, I think a' will plough up
all, if there is not better directions.
GOWER
The Duke of Gloucester, to whom the order of the
siege is given, is altogether directed by an
Irishman, a very valiant gentleman, i' faith.
FLUELLEN
It is Captain Macmorris, is it not?
GOWER
I think it be.
FLUELLEN
By Cheshu, he is an ass, as in the world: I will
verify as much in his beard: be has no more
directions in the true disciplines of the wars, look
you, of the Roman disciplines, than is a puppy-dog.
Enter MACMORRIS and Captain JAMY
GOWER
Here a' comes; and the Scots captain, Captain Jamy, with him.
FLUELLEN
Captain Jamy is a marvellous falourous gentleman,
that is certain; and of great expedition and
knowledge in th' aunchient wars, upon my particular
knowledge of his directions: by Cheshu, he will
maintain his argument as well as any military man in
the world, in the disciplines of the pristine wars
of the Romans.
JAMY
I say gud-day, Captain Fluellen.
FLUELLEN
God-den to your worship, good Captain James.
GOWER
How now, Captain Macmorris! have you quit the
mines? have the pioneers given o'er?
MACMORRIS
By Chrish, la! tish ill done: the work ish give
over, the trompet sound the retreat. By my hand, I
swear, and my father's soul, the work ish ill done;
it ish give over: I would have blowed up the town, so
Chrish save me, la! in an hour: O, tish ill done,
tish ill done; by my hand, tish ill done!
FLUELLEN
Captain Macmorris, I beseech you now, will you
voutsafe me, look you, a few disputations with you,
as partly touching or concerning the disciplines of
the war, the Roman wars, in the way of argument,
look you, and friendly communication; partly to
satisfy my opinion, and partly for the satisfaction,
look you, of my mind, as touching the direction of
the military discipline; that is the point.
JAMY
It sall be vary gud, gud feith, gud captains bath:
and I sall quit you with gud leve, as I may pick
occasion; that sall I, marry.
MACMORRIS
It is no time to discourse, so Chrish save me: the
day is hot, and the weather, and the wars, and the
king, and the dukes: it is no time to discourse. The
town is beseeched, and the trumpet call us to the
breach; and we talk, and, be Chrish, do nothing:
'tis shame for us all: so God sa' me, 'tis shame to
stand still; it is shame, by my hand: and there is
throats to be cut, and works to be done; and there
ish nothing done, so Chrish sa' me, la!
JAMY
By the mess, ere theise eyes of mine take themselves
to slomber, ay'll de gud service, or ay'll lig i'
the grund for it; ay, or go to death; and ay'll pay
't as valourously as I may, that sall I suerly do,
that is the breff and the long. Marry, I wad full
fain hear some question 'tween you tway.
FLUELLEN
Captain Macmorris, I think, look you, under your
correction, there is not many of your nation--
MACMORRIS
Of my nation! What ish my nation? Ish a villain,
and a bastard, and a knave, and a rascal. What ish
my nation? Who talks of my nation?
FLUELLEN
Look you, if you take the matter otherwise than is
meant, Captain Macmorris, peradventure I shall think
you do not use me with that affability as in
discretion you ought to use me, look you: being as
good a man as yourself, both in the disciplines of
war, and in the derivation of my birth, and in
other particularities.
MACMORRIS
I do not know you so good a man as myself: so
Chrish save me, I will cut off your head.
GOWER
Gentlemen both, you will mistake each other.
JAMY
A! that's a foul fault.
A parley sounded
GOWER
The town sounds a parley.
FLUELLEN
Captain Macmorris, when there is more better
opportunity to be required, look you, I will be so
bold as to tell you I know the disciplines of war;
and there is an end.
Exeunt
Irish History and Shakespeare: The tempestous relationship between england and Ireland
The mayor and all his brethren in best sort,
Like to the senators of the antique Rome,
With the plebeians swarming at their heels,
Go forth and fetch their conquering Caesar in:
As, by a lower but loving likelihood,
Were now the general of our gracious empress,
As in good time he may, from Ireland coming,
Bringing rebellion broached on his sword,
Henry V, Act V Chorus
James Shapiro in his excellent book, A Year In The Life Of William Shakespeare, 1599, posits that contemporary affairs in Ireland might have inspired some of Shakespeare’s greatest plays in including Richard II, Henry V, and Julius Caesar. In 1594 the Earl of Tyrone began a rebellion in Ireland against the English, and in 1599, Queen Elizabeth dispatched the ambitious and chivalrous Earl of Essex to quell it. As you can see in the quote above, Shakespeare mentions Essex’s fight in his play of Henry V, which probably premiered at around the same time Essex was in Ireland.
The audience may have been watching Henry conquer France, but many would have been thinking about Elizabeth’s struggle to conquer Ireland.
BBC Radio 4 Extra – Shakespeare’s Restless World, Ireland: Failures in the Present – Transcript – Shakespeare’s Restless World – Programme 7
Though King Henry successfully conquered and united England and France, Essex failed spectacularly, and Elizabeth was deeply embarrassed by the whole scenario. She was also deeply alarmed by the popularity of Shakespeare’s tragedy Richard II, which shows onstage the deposing and killing of a king who had no children and failed to quell a rebellion in Ireland.
Elizabeth was worried about her subjects but she was also very worried about Essex overseas. Everyone, (including Shakespeare), remembered that 2,000 years ago, Julius Caesar went from him the Senate’s Consul General to dictator by amassing an army, then threatening to invade Rome under the pretense of helping to quell a foreign invasion. Caesar made his name by subjugating tribes in Gaul (modern-day France), and the Senate was worried that he would come home and use his army for a military coup. Look at the expressions on the faces of Cicero and Brutus when they see Caesar coming home in triumph in this scene from the HBO series Rome.
Elizabeth repeatedly attempted to curb Essex’s power while he was fighting in Ireland; she refused to give the Earl more troops for fear that he might be staging a potential coup. Her fears would later be proven right when in 1602, Essex attempted to head a rebellion and take the Crown for himself, but not before one of Essex’s friends commissioned Shakespeare’s company to portray the deposing and killing of King Richard II. Essex was trying to turn himself from a failed Henry V to a victorious Henry IV, and his queen into Richard II.


Shakespeare might have been inspired to write Julius Caesar after being an unwitting pawn in the political drama between Essex and the queen, and might have even created the character of Cinna the Poet as an analog for Shakespeare himself. In the play, Cinna the poet is mistaken for one of the conspirators by an angry mob and is murdered in the street. Perhaps Shakespeare created Cinna the Poet as a way of coping with the fear he must have had that people might mistake him for a radical, after his play Richard II briefly made him a walking target for those opposed to Essex’s rebellion. In any case, Julius Caesar eloquently documents the kind of anxiety of not knowing who could be trusted when it comes to politics, whether it be a populist warrior like Julius Caesar or Essex, or the Queen, privy council, or indeed Roman senate, and the whole thing started from a failed attempt to quell a rebellion in Ireland.
In summation, even though Shakespeare sets no plays in Ireland, Irish history and Irish culture are everywhere in his plays. England and Ireland are I are indeed separate islands but the cultural exchange between England and Ireland has inspired Shakespeare and many other great writers for centuries. After all Shakespeare’s most famous honorific, ‘the Bard of Avon’ comes from an ancient Irish tradition of semi-mystical poets, who in Irish folklore, were able to see the future and glimpse worlds that are unseen to ordinary mortals. What Shakespeare really felt about Ireland we don’t know but we do him but he does owe the Irish people a lot of thanks, and on this Saint Patrick’s day, I honor their contribution to him and to him all the world
References:
Shapiro, James. A Year In the Life Of William Shakespeare, 1599. Chapter 6: Things Dying and Things Reborn.























 • Plague carts like in Monty Python (Dreary) carried plague bodies out of the city and burned them.
• Plague carts like in Monty Python (Dreary) carried plague bodies out of the city and burned them.



































 As I have written before, Richard claims the throne by manipulating everyone in the British political machine- stoking hatred among the nobles, while trying to appear as a pious, humble man to the common people. Because of his years on reality television and experience as a businessman, even I must admit Trump has a gift at manipulating people’s perceptions and playing the part of a man of the people:
As I have written before, Richard claims the throne by manipulating everyone in the British political machine- stoking hatred among the nobles, while trying to appear as a pious, humble man to the common people. Because of his years on reality television and experience as a businessman, even I must admit Trump has a gift at manipulating people’s perceptions and playing the part of a man of the people:




