
Subscribe to continue reading
Subscribe to get access to the rest of this post and other subscriber-only content.



Subscribe to get access to the rest of this post and other subscriber-only content.








O ceremony, show me but thy worth!
What is thy soul of adoration?
Art thou aught else but place, degree and form,
Creating awe and fear in other men?
Wherein thou art less happy being fear'd
Than they in fearing.
What drink'st thou oft, instead of homage sweet,
But poison'd flattery? O, be sick, great greatness,
And bid thy ceremony give thee cure!
Think'st thou the fiery fever will go out
With titles blown from adulation?
Will it give place to flexure and low bending?
Canst thou, when thou command'st the beggar's knee,
Command the health of it? No, thou proud dream,
That play'st so subtly with a king's repose;
I am a king that find thee, and I know
'Tis not the balm, the sceptre and the ball,
The sword, the mace, the crown imperial,
The intertissued robe of gold and pearl,
The farced title running 'fore the king,
The throne he sits on, nor the tide of pomp
That beats upon the high shore of this world,
No, not all these, thrice-gorgeous ceremony Henry V, Act IV, Scene i.
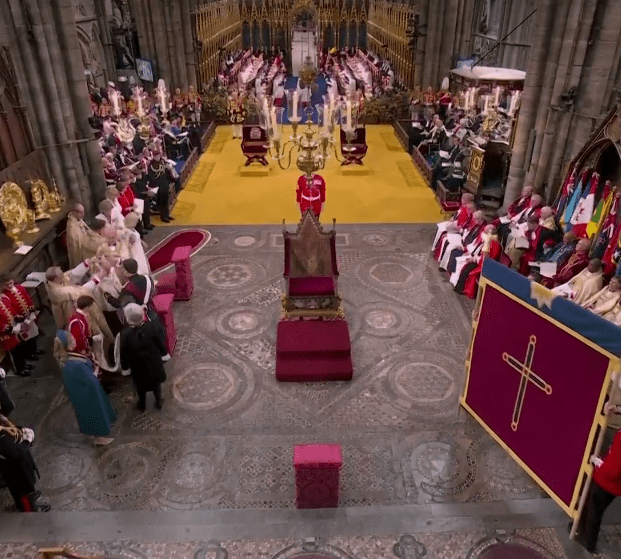
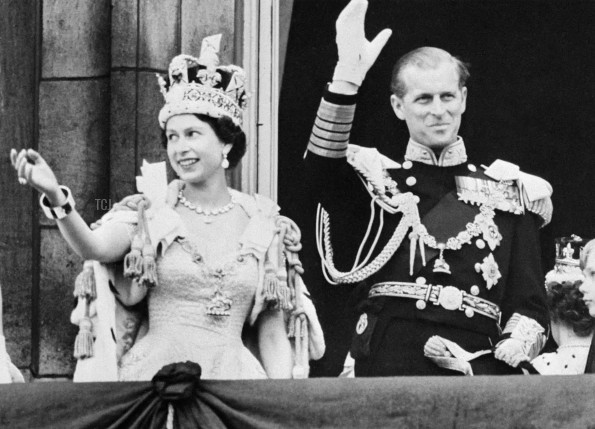
As this quote from Shakespeare's Henry V, there are many different cermonial customs and adornments that the British monarchs have used to adorn and elevate their kings and queens. Today I'm going to compare and contrast King Charles III and his mother Queen Elizabeth II, then I'll compare these coronations with the monarch who lived during most of Shakespeare's life: Queen Elizabeth I.
All my information for this section comes from this fascinating article from the Washington Post, which compares and contrasts King Charles’ coronation on May 6th, 2022, with his mother’s, which occurred on June 2, 1953:

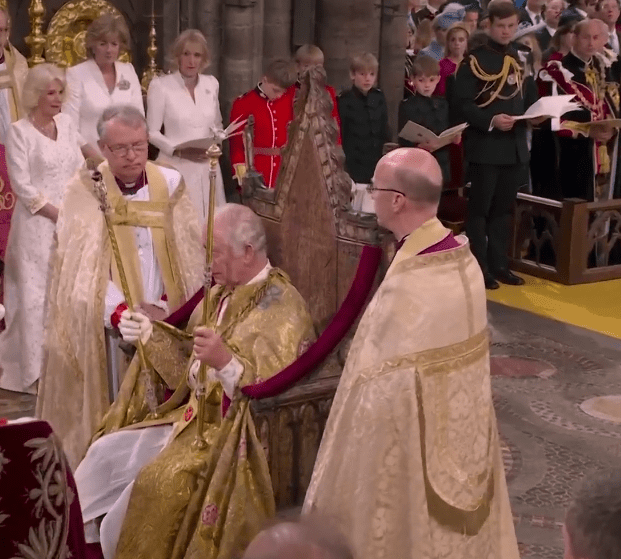
Both Charles and Elizabeth were anointed with holy oil- an ancient tradition signifying God’s favor. The tradition goes all the way back to the Bible, where the book of First Kings details the procedure of anointing King Solomon:
And the king said to them, “Take with you the servants of your lord and have Solomon my son ride on my own mule, and bring him down to Gihon.
And let Zadok the priest and Nathan the prophet there anoint him king over Israel. Then blow the trumpet and say, ‘Long live King Solomon!’ You shall then come up after him, and he shall come and sit on my throne,
1 Kings Chapter 1, Verses 33-35
King George the Third commissioned composer Georg Friedrich Handel (famous for “The Messiah”) to write an anthem for his coronation based on this Biblical passage in 1761 This song has been a tradition during English coronations for the past 300 years, and as you can see in the video below, it was played when King Charles and Queen Elizabeth were privately anointed behind the canopy you see below.
The scepter is called the Sovereign’s Scepter and it is on display in the Tower of London as part of the Crown Jewels. For more information, go to Royal Collection.org:
https://www.rct.uk/collection/themes/Trails/the-crown-jewels-coronation-regalia


The ball in this passage refers to the globus cruciger or ‘the orb and the cross.’ This is a symbol of the king’s status as the head of the Church Of England, which began with Elizabeth I’s father, Henry VIII. The orb telegraphs Christ as the true ruler of the world, and the English monarch as his representative on Earth.

A mace used to be a concussive weapon used in battle against knights in shining armor. Since armor is hard to penetrate, medieval warriors tried to cause blunt force trauma and concussion in their enemies using maces. Since those more violent beginnings, the mace has evolved into a symbol of the King’s power and is used at the opening of Parliament. There are three swords that lords used to herald the King during the coronation- the two swords of Justice, and the Curtana or ‘Sword of Mercy,’ so called, because its blade is broken, making it a ceremonial object of peace, rather than a practical weapon.

King Charles’ own sword is called the Sword of State- it is a steel sword gilded with silver, and the handle is wooden, gilded with gold. It symbolizes the monarch’s commitment to knightly virtues, and it is used to create people as knights.

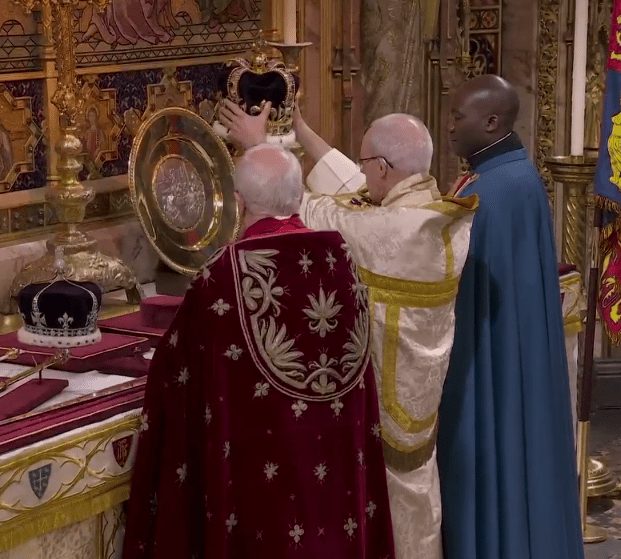
St. Edward’s crown is adorned with diamonds, furs, and over 2,000 diamonds! This crown, along with the sword of state, dates back to the 1660s, after the monarchy was briefly abolished, though the crown still has had its share of problems over the centuries, including being stolen!
Much like how during graduation ceremonies people wear special robes to signify the transition from one state of being to another, British monarchs have worn multiple robes to show their apotheosis from a prince to the sovereign head of the country.
The robe of Estate is the long, sumptuous robe of the sovereign; a symbol of his or her wealth. Charles wore his at the end of the ceremony after the crown was placed on his head.
Traditionally, the Robe of Estate is a very specific shade of purple called Tyrian Purple. It is again, a symbol of wealth because it was very labor-intensive and expensive to produce. This is one of the reasons why purple is a color associated with wealth and status:


Elizabeth’s purple Robe of Estate will now be worn by Queen Camilla, Charles’ wife. It is 6 1/2 meters long, weighs 15 pounds, and took 12 seamstresses 3,500 hours to complete, (source: Historic UK).

The oldest part of the ceremony will without question be the throne- a plain-looking piece of oak that is over 700 years old! St. Edward’s Throne has been part of coronation ceremonies since King Edward I, (aka Edward Longshanks from Braveheart) in around 1200 AD. Surely there is no greater symbol of royal continuity- the monarchs in Shakespeare’s history plays actually sat on this throne. Any king or queen who touches this piece of furniture must get a sense of the ancient traditions of the monarchy.


It’s been a tradition ever since the Middle ages for the new king or queen to travel from their home palace through the county so people can see them on their way to be crowned at Westminster Abbey. Long ago, this was a multi-day journey full of public festivals and entertainment that allowed the whole country to get a rare glimpse of the new monarch. By contrast, King Charles and Queen Camila only traveled 1.3 miles from Buckingham Palace to Westminster.


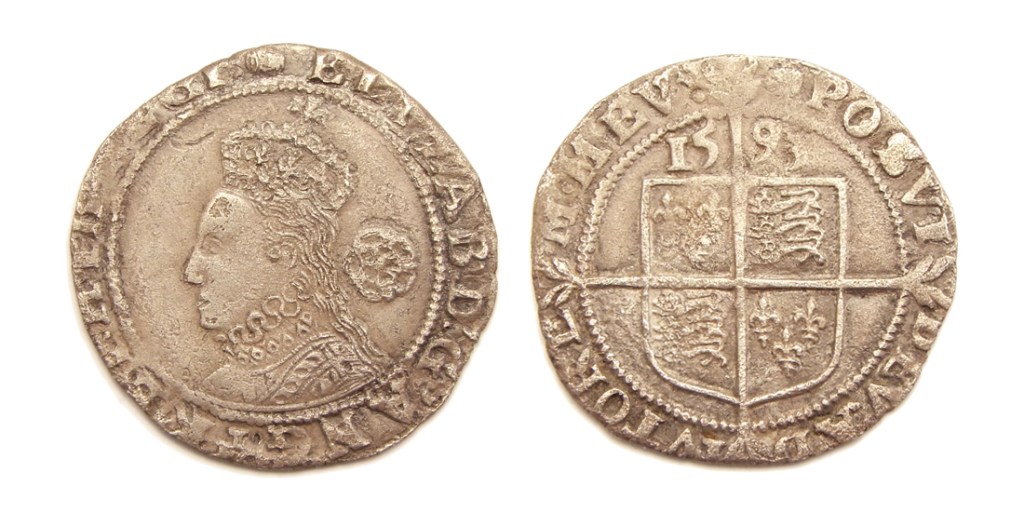
After the death of Mary the First, Elizabeth’s sister,



Like her namesake and the new king, Queen Elizabeth I was crowned at Westminster on January 15, 1558. Unlike them, however, the ceremony was performed in Latin and English by a Catholic bishop. Obviously, since Elizabeth was crowned during the Protestant Reformation, there was a lot of controversy about the liturgy. Some accounts aren’t sure what parts of the Catholic were read, but we do know Elizabeth took the oath, wore a similar golden robe to Charles and Elizabeth II, and was given the balm and scepter just like them. Here is a primary source account from an ambassador from the town of Mantua, Italy:
“The Queen was received under the canopy by the Archbishop and another Bishop, they having previously perfumed her with incense, giving her the holy water and the pax, the choristers singing; then the Earl of Rutland followed her Majesty with a plain naked sword without any point, signifying Ireland, which has never been conquered; then came the Earl of Exeter with the second sword; the third was borne by Viscount Montagu; the Earl of Arundel, having been made Lord Steward and High Constable for that day, carried the fourth (sword) of royal justice, with its gilt scabbard loaded with pearls. The orb was carried by the Duke of Norfolk, Lord Marshal, and in advance were knights clad in the ducal fashion, carrying the three crowns, they being the three Kings-at-arms; they bore the three sceptres, with their three crowns of iron, of silver, and of gold on their heads, and in their hands three naked iron swords, signifying the three titles of England, France, and Ireland..”
— Il Schifanoya, royal ambassador from Mantua

‘And whereas your request is that I should continue your good lady and be Queen, be ye ensured that I will be as good unto you as ever Queen was unto her people. No will in me can lack, neither do I trust shall there lack any power. And persuade yourselves that for the safety and quietness of you all I will not spare if need be to spend my blood. God thank you all.’ _Queen Elizabeth I


https://www.rct.uk/collection/404386/queen-elizabeth-ii-1926-2022-in-coronation-robes

For Shakespeare’s birthday, I thought I’d re-visit one of my most popular posts, especially since the Royal Shakespeare Company is celebrating by putting on an adaptation of Maggie O’Farrell’s novel Hamnet:
Just like his famous father, we know very little about the life of Hamnet Shakespeare. Since infant mortality rates were high, we don’t know his exact birthday, only that he was baptized on February 2nd, 1582. Like most 11-year old boys, he probably had started going to school at the King Edward Grammer School, the same as his father. This means he spent long hours away from his parents learning to read and write in Latin and Greek. When he was home, he lived with his mother, his two sisters, and his grandparents in the house of Henley Street.
https://www.kes.net/about-us/history-of-the-school/
O’Farrel portrays the boy Hamnet as sensitive and somewhat lonely, which makes sense, since he probably didn’t see his father for long periods of the year; Will Shakespeare spent much of the year writing, going on tour, and performing at the Globe- he commuted from London to Stratford for most of the year. He probably only came around during Lent, Christmas, and times of plague when the theaters were closed.

Never mind what I know. You must go.” She pushes at his chest, putting air and space between them, feeling his arms slide off her, disentangling them. His face is crumpled, tense, uncertain. She smiles at him, drawing in breath. “I won’t say goodbye,” she says, keeping her voice steady. “Neither will I.” “I won’t watch you walk away.” “I’ll walk backwards,” he says, backing away, “so I can keep you in my sights.” “All the way to London?” “If I have to.” She laughs. “You’ll fall into a ditch. You’ll crash into a cart.” “So be it.
O’Farrell

The novel portrays Anne Shakespeare realizing that her husband is stifled and unhappy living with his parents in Stratford, and so she suggests to his father that he go to London to ‘expand the family business,’ though in reality, she wants him to go to make his fortune and find more fulfilling work. Scholars have wondered for years how Shakespeare got his start in theater- as a man with children he was legally unable to become an apprentice, and as a glover’s son from Stratford, he didn’t know anyone in London. O’Farrell solves the mystery by making him start out as a costume maker and mender for a theater company, who later became a writer and actor.
This idea of Shakespeare starting out as the company’s glove mender actually has some historical merit- records from the time confirm that many playwrights and actors were also local artisans. Men like John Webster, Richard Tarlton, Edward Kyneston, and even Richard Burbage were skilled drapers, textile merchants, haberdashers (men’s tailors) and ( like the Bottom in “A Midsummer Night’s Dream,”) some of these men were weavers-turned actors (Source: Anna Gonzales) So it’s entirely possible that Shakespeare started in London by selling gloves to theaters, before selling his plays.
When Will moved to London, he lived in a number of locations throughout the city, probably because it wasn’t a safe place. Theaters were located in the same districts as bear baiting and brothels, so Will probably had to move to get away from bad neighborhoods, as this video from The History Squad illustrates:
A glover will only ever want the skin, the surface, the outer layer. Everything else is useless, an inconvenience, an unnecessary mess. She thinks of the private cruelty behind something as beautiful and perfect as a glove.
Hamnet

https://www.shakespeare.org.uk/explore-shakespeare/blogs/shakespeare-100-objects-pair-gloves/
Almost immediately after Will leaves, Anne is full of remorse. She knows his work in London will consume him and his success will make the distance between him and her even greater.
She walks back, more slowly, the way she came. How odd it feels, to move along the same streets, the route in reverse, like inking over old words, her feet the quill, going back over work, rewriting, erasing. Partings are strange. It seems so simple: one minute ago, four, five, he was here, at her side; now, he is gone. She was with him; she is alone. She feels exposed, chill, peeled like an onion.
He wants to tear down the sky, he wants to rip every blossom from that tree, he wishes to take a burning branch and drive that pink-clad girl and her nag over a cliff, just to be rid of them, to clear them all out of his way. So many miles, so much road stands between him and his child, and so few hours left.
Hamnet
As I’ve said in previous posts, Shakespeare survived three epidemics of Plague; one in 1563, (before he was born), one in 1593, and one in 1603. In O’Farell’s novel, the germs that kill Hamnet came not from a massive outbreak, but a few germs that were transported in a box that his sister had the misfortune of opening. This frightful passage shows the grim tenacity and eve-present fear that, while England expanded and became more interconnected with the world, it also brought death and disease to and from the rest of Europe.
In the book, the plague germs that infect Judith and later Hamnet, lie inside a box with some glass beads that the Shakespeare’s ordered from Italy to decorate a pair of fancy gloves. As this video from National Geographic shows, trade routs then as now are prime spreaders of disease and even one ship that slips by can turn any box of goods into a Pandora’s Box, waiting for a poor unsuspecting girl like Judith to release it unto the world.
He can feel Death in the room, hovering in the shadows, over there beside the door, head averted, but watching all the same, always watching. It is waiting, biding its time. It will slide forward on skinless feet, with breath of damp ashes, to take her, to clasp her in its cold embrace, and he, Hamnet, will not be able to wrest her free.
Hamnet

In the novel, Hamnet somehow takes the plague away from his sister and dies in her place. Though it is hardly conclusive, I do find it interesting that Shakespeare stopped writing comedies about twins for another four years after Hamnet’s death, until he wrote Twelfth Night, which unlike earlier comedies like The Comedy of Errors, has a pair of twins mourning each other’s apparent death. They seem to share one soul, and one tries to resurrect the other, like Viola mourning her brother by, (in a sense), becoming her brother.
What should I do in Ilyria? My brother is in Elysium
Viola- “Twelfth Night”, Act I, Scene ii.
ELIZABETHAN FUNERAL CUSTOMS
In the book, Anne makes a winding sheet for her son. This was a cloth of linen or wool that was wrapped around dead bodies, since at the time, coffins were re-used. This must have been a somber and deeply upsetting activity for Anne.

As this quote from “The Evolution of the English Shroud” illustrates, the act of making a winding sheet was a sort of sad family responsibility, a way of ensuring that your loved ones die with dignity, and Anne clearly takes the task of making one very seriously.
The 16th-century shroud for the poor and lower middle classes was a large sheet that was gathered at the head and feet, and tied in knots at both ends, covering every part of the body. It resembled earlier Medieval practices and was a functional, yet modest way of preserving the deceased’s dignity. It was also economical, with very little cost involved, as the burial sheet was usually taken from the family home. At this point, linens dominated as the material of choice; after all, it was a biblical tradition as Jesus was wrapped in a linen cloth. Linen was also considered more fashionable than wool.
Coffin Works Archive

She discovers that it is possible to cry all day and all night. That there are many different ways to cry: the sudden outpouring of tears, the deep, racking sobs, the soundless and endless leaking of water from the eyes. That sore skin around the eyes may be treated with oil infused with a tincture of eyebright and chamomile. That it is possible to comfort your daughters with assurances about places in Heaven and eternal joy and how they may all be reunited after death and how he will be waiting for them, while not believing any of it. That people don’t always know what to say to a woman whose child has died. That some will cross the street to avoid her merely because of this. That people not considered to be good friends will come, without warning, to the fore, will leave bread and cakes on your sill, will say a kind and apt word to you after church, will ruffle Judith’s hair and pinch her wan cheek.
The most unique thing about this novel is how it shows the interdependence of women in Elizabethan society. Since Shakespeare spends most of the novel away from Anne, her support system mostly comes from Will’s mother Mary, as well as Anne’s daughters, her sister, and all the other women of the town. Nowadays we do most of our socialization online and barely know our own neighbors, but in the 1590s, especially for women, community was a way of building strength where women got through things like childbirth, loss, the managing of households, and many other difficulties through their relationships with other women. This video below shows the kinds of home remedies that women would share and later write down during the Tudor period:
Once Hamnet dies, Will buys her a new house, New Place so she isn’t forced to live with his parents and no longer has to live in the house where her son died. But Will’s success comes with a price- he still has to leave for London. he offers to move them there but Agnes won’t hear of it. This solves the riddle of why Shakespeare commuted between town and country for his entire career- she knows the plague that took her son literally came from London, and she won’t risk losing her daughter as well. She probably also sees London like another woman that took her husband away as well, and therefore refuses to look it in the face.
It is no matter,” she pants, as they struggle there, beside the guzzling swine. “I know. You are caught by that place, like a hooked fish.” “What place? You mean London?” “No, the place in your head. I saw it once, a long time ago, a whole country in there, a landscape. You have gone to that place and it is now more real to you than anywhere else. Nothing can keep you from it. Not even the death of your own child. I see this,” she says to him, as he binds her wrists together with one of his hands, reaching down for the bag at his feet with the other. “Don’t think I don’t.”
O’Farrell, Hamnet.
I mean’, he says, ‘that I don´t think you have any idea what it is like to be married to someone like you.’
Hamnet
‘Like me?’
‘Someone who knows everything about you, before you even know it yourself. Someone who can just loo at you and divine your deepest secrets, just with a glance. Someone who can tell what you are about to say- and what you might not- before you say it. It is’ he says, ‘both a joy and a curse.
The ugly truth that O’Farrell highlights in Hamnet is that it must have been very hard for the Shakespeares to endure Hamnet’s death, especially since Will was probably not there when it happened, and probably didn’t stay around long after burying his son. It must have been catastrophic on his marriage, sort of like this tragic moment in the musical Hamilton, where the couple mourns the loss of their son, who died in a duel trying to defend his father’s honor.
Agnes is a woman broken into pieces, crumbled and scattered around. She would not be surprised to look down, one of these days, and see a foot over in the corner, an arm left on the ground, a hand dropped to the floor. Her daughters are the same. Susanna’s face is set, her brows lowered in something like anger. Judith just cries, on and on, silently; the tears leak from her and will, it seems, never stop. — How were they to know that Hamnet was the pin holding them together? That without him they would all fragment and fall apart, like a cup shattered on the floor?
Maggie O’Farrell, Hamnet
Though Anne is angry at Will for a while, she does eventually forgive him, as evidenced by another solved historical mystery. In Shakespeare’s will he gives his wife “My second-best bed, with the furniture,” which O’Farell explains, is their marriage bed. The best bed was the one they gave to guests and was therefore newer. In the book, Will offers to replace it after Hamnet dies, but Anne won’t hear of it; although she partially blames Will for Hamnet’s death, she still loves him and her love is stronger than her grief, as is her love for her surviving daughters.

What is the word, Judith asks her mother, for someone who was a twin but is no longer a twin?
Her mother, dipping a folded, doubled wick into heated tallow, pauses, but doesn’t turn around.
If you were a wife, Judith continues, and your husband dies, then you are a widow. And if its parents die, a child becomes an orphan. But what is the word for what I am?
I don’t know, her mother says.
Judith watches the liquid slide off the ends of the wicks, into the bowl below.
Maybe there isn’t one, she suggests.
Maybe not, says her mother

At the end of the book, Shakespeare plays the Ghost of Hamlet’s father, and writes Hamlet as a tribute to his late son. We don’t know for a fact that the real William Shakespeare did this but Stratford legend says that Shakespeare played the Ghost of Hamlet’s father onstage, and this has captivated the imagination of authors and scholars alike. In any case, as Stephen Greenblatt says in his book Will In The World, Shakespeare’s father’s health faded around the same time that he wrote Hamlet. it must have been hard for Shakespeare to write a name that was one letter away from his son’s over and over again. Hamlet is Shakespeare’s longest play, and the titular character has over 40% of the dialogue, so it must have been haunting at the very least for Shakespeare to have to write his son’s name nearly 4,000 times.
Whatever he determined at the time, Shakespeare must have still been brooding in late 1600 and early 1601, when he sat down to write a tragedy whose doomed hero bore the name of his dead son. His thoughts may have been intensified by news that his elderly father was seriously ill back in Stratford, for the thought of his father's death is deeply woven into the play. And the death of his son and the impending death of his father--a crisis of mourning and memory--could have caused a psychic disturbance that helps to explain the explosive power and inwardness of Hamlet.Greenblatt,
2004, p. 8)
In the book, Anne secretly goes to London to see Hamlet onstage and is overcome with emotion. Not only does Will play a ghost as tribute to his dying father, not only does he put his son’s name onstage, he directs the actor playing Hamlet to affect his own son’s mannerisms and gestures, to use theater to bring his son back from the dead. Anne is both appalled and moved by this act- Hamnet is dead, but his story is now immortal.
O’ Farrell has done a fantastic job of taking what little we know about the Shakespeare’s lives, infusing them with some clever inferences from the plays of Will Shakespeare, and finally fleshing them out with her own Shakespearean knowledge of the human heart- how it feels to bury someone, how it feels to go through trauma and what it’s like to be part of a family and to truly love someone, even though they often fail to properly love you back. As the end of the book implies, maybe Will didn’t intend to immortalize his son and share his powers of theatrical resurrection with the world, maybe this was just his way of apologizing to the love of his life. To try to make amends for the time he lost and to express a wish that he could give her son back to her, which in a way, he does:
Hamlet, here, on this stage, is two people, the young man, alive, and the father, dead. He is both alive and dead. Her husband has brought him back to life, in the only way he can. As the ghost talks, she sees that her husband, in writing this, in taking the role of the ghost, has changed places with his son. He has taken his son’s death and made it his own; he has put himself in death’s clutches, resurrecting the boy in his place. “O horrible! O horrible! Most horrible!” murmurs her husband’s ghoulish voice, recalling the agony of his death.
O’Farrell, “Hamnet”
Journals
Bray, Peter. “Men, loss and spiritual emergency: Shakespeare, the death of Hamnet and the making of Hamlet.” Journal of Men, Masculinities and Spirituality, vol. 2, no. 2, June 2008, pp. 95+. Gale Literature Resource Center, link.gale.com/apps/doc/A189052376/LitRC?u=pl9286&sid=bookmark-LitRC&xid=ea79f235. Accessed 20 Apr. 2023.
Period Documents
Document-specific information
Creator: Holy Trinity Church, Stratford-upon-Avon
Title: Parish Register of Holy Trinity Church, Stratford-upon-Avon
Date: 1558-1776
Repository: The Shakespeare Birthplace Trust, Stratford-upon-Avon, UK
Call number and opening: DR243/1: Baptismal register, fol. 22v
View online bibliographic record
Web
King Edward Grammar School History: https://www.kes.net/about-us/history-of-the-school/
Shakespeare’s Birthplace Trust- The Second Best Bed: https://www.shakespeare.org.uk/explore-shakespeare/shakespedia/william-shakespeare/second-best-bed/
Coffin Archive.org- The Evolution of the English Shroud: From Single Sheet To Draw-Strings and Sleeves: http://www.archive.coffinworks.org/uncategorised/the-evolution-of-the-english-shroud-from-single-sheet-to-draw-strings-and-sleeves/
I just got a copy of the Shakespeare Game in honor of Shakespeare’s birthday! Here are a few reviews and videos!
https://boardgamegeek.com/boardgame/365920/shakespeare-game

This clip from Mel Brooks’ comic masterpiece History of the World, Part I, has the writer/director perform as Comicus, a ‘stand-up philosopher’ from Ancient Rome- a philosopher who is basically a stand-up comic. As you’ll see, unlike clowns, most of Shakespeare’s fools basically fulfill this role- to satirize and make fun of people and institutions.
A fool is the renaissance version of a minstrel- an official royal entertainer who worked at royal courts. A clown is a comic part in a play. The often danced, sang, and did improv comedy. To illustrate the difference, here’s a short video about the life of Henry VIII’s favorite fool- Will Sommers
All of Shakespeare’s fools and clowns are based on ancient Italian sources-from the Roman comedies of Plautus and Terrence to the improvised comedy known as Commedia Del ‘ Arte
Commedia is based on stock character types that Shakespeare adapted and fleshed out- Arlequinno became the constantly hungry Dromio, (among others), while Capitano became Falstaff and Pistol. Even Shylock has remnants of Brighella in his DNA. According to Dario Fo in his book: Manuale Minimodell’Attore, Shakespeare adapted stock characters from commedia to be his clowns, and sarcastic characters called sots, who commented on the action to become his fools (Fo, 107)

Despite his strength and skill as a dancer, Kempe specialized in playing oafish buffoons like Dogberry in Much Ado About Nothing, Falstaff in the Henry IV plays, and Peter in Romeo and Juliet. In the Second Quarto edition of Romeo and Juliet, you can see in the stage directions “Enter Will Kempe,” right before Peter speaks:

According to Will In the World by Steven Greenblatt, Kempe and Shakespeare had a falling out in the late 1590s, which many scholars have assumed might have been due to Shakespeare’s distaste for clowns wasting time with jokes that bogged down the play:
Hamlet:
Let those that play your
clowns speak no more than is set down for them. For there
be of them will themselves laugh, to set on some
quantity of barren spectators to laugh too. Though in the
meantime, some necessary question of the play be then
to be considered. That's villainous, and shows a most pitiful
ambition in the fool that uses it. Hamlet, Act III, Scene ii.
Kempe, for his part, seemed a little big for his britches; he and his fellow clowns seemed to think that Shakespeare's scripts were just vehicles for his own jokes and songs (Reynolds, 247). He then sold his share in the Chamberlain's Men, derriding them in print as "My notable Shake-rags," and then staged a publicity stunt where he danced across England!

Kempe’s replacement was Robert Armin, an accomplished writer and singer, who specialized in playing satirical Fool roles. Armin appeared in several Shakespearean plays after 1599.
Unlike Kempe, Armin’s characters are essential to the plot of the play, and his jokes support the themes and ideas of the plays themselves. As Feste in Twelfth Night, Armin makes jokes that make fun of the overly-serious Orsino and Countess Olivia:
Feste. Good madonna, why mournest thou?
Olivia. Good fool, for my brother's death.
Feste. I think his soul is in hell, madonna.
Olivia. I know his soul is in heaven, fool.
Feste. The more fool, madonna, to mourn for your brother's
soul being in heaven. Take away the fool, gentlemen. Twelfth Night, Act I, Scene v.

Sometimes Armin’s characters are satirical mirrors of Elizabethan society; in As You Like It, Touchstone the Fool mocks the culture of dueling; implying that there are hundreds of loopholes that a gentleman may use to challenge a man to a duel, without actually fighting.
Perhaps Armin’s greatest comic creation was The Fool in King Lear; the ultimate satirist who makes fun of the king’s foolish choices. He tries to talk sense to the increasingly mad king, until he vanishes entirely, and Lear himself starts making fool-like cracks at the audience:
Lear Thou hast seen a
farmer's dog bark at a beggar?
Earl of Gloucester. Ay, sir.
Lear. And the creature run from the cur? There thou mightst behold
the great image of authority: a dog's obeyed in office.
The usurer hangs the cozener.
Through tatter'd clothes small vices do appear;
Robes and furr'd gowns hide all. Plate sin with gold,
And the strong lance of justice hurtless breaks;
Arm it in rags, a pygmy's straw does pierce it.
None does offend, none- I say none! Get thee glass eyes
And, like a scurvy politician, seem
To see the things thou dost not. King Lear, Act IV, Scene vi.
Through realizing his own foolishness, Lear recovers his sanity, and makes peace with his daughter, which beautifully shows the importance of fools, clowns, and satirists; to question ourselves, to sharpen our critical thinking, and to endure hardships with good humor. Therefore on this April Fools Day, I say,
“Here’s to the fools, to folly, to farce. Let them push the wealthy on the ar— APRIL FOOLS!”
Best, Michael. “Shakespeare’s Actors: Will Kempe” Internet Shakespeare Editions, University of Victoria, 28 Sept. 2016, ise.uvic.ca/Foyer/citing. Accessed 30 Sept. 2023.
Fo, Dario. Manuale Minimodell’Attore (English: “The Tricks Of the Trade” Translated by Joe Farrell, 1991. Accessed online at Google Books: https://www.google.com/books/edition/The_Tricks_of_the_Trade/akEJ9Ew9GaoC?hl=en&gbpv=1. 29 March. 2023.
I teach a class specifically on Shakespeare’s comedies where I’ll talk a lot about the way Shakespeare writes clowns. I’ll also delve into the history of Commedia Del’Arte and how it influenced Shakespeare’s characters! For more information, visit http://www.outschool.com


Happy Black History Month Everyone! Today I’m paying tribute to a great actor and activist, Mr. Ira Aldridge (1807-1867).
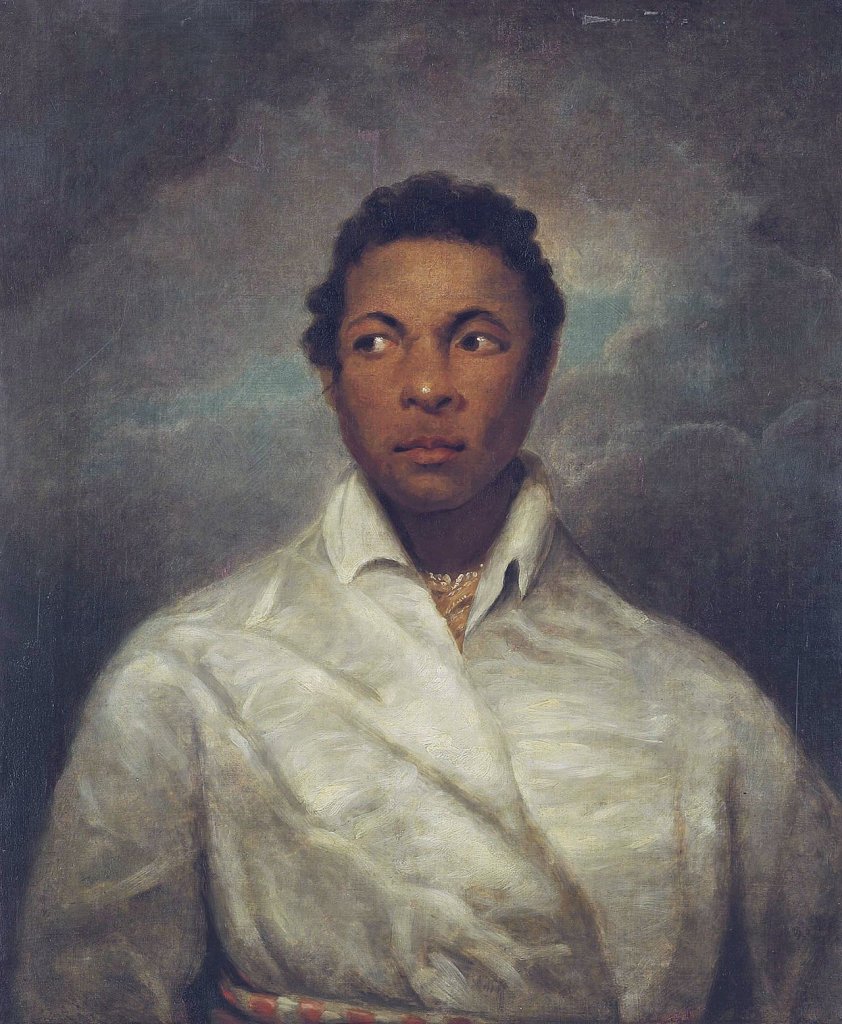

Mr Ira Aldridge was not only a great actor but also an influential figure in the abolitionist movement. He rose from the depths of discrimination and dehumanization to become a famous, respected international actor. Furthermore, his life was marked by creating new opportunities for himself and other people of color.

True feeling and just expression are not confined to any clime or colour.
Ira Adridge
Born in New York in 1807, Mr. Aldridge had dreams to found an all-black theater even as a teenager. His first job was with William Brown’s African Theatre, the first African American theater company. However, discrimination and racism blocked Mr. Aldridge from success in New York, when another theater manager “hired thugs to beat up the actors”. The theatre subsequently burned down and the actors were abused by the New York police. Undaunted, Aldridge decided to take his talents to England, boarding a ship, and arriving in the early 1820s. (Howard, qtd in Thorpe 1). Even though he faced discrimination and violence as a child, Mr. Aldridge would not be deterred. Soon his skill as a Shakespearean actor would soon command respect from all.3.) He refused to be defined by the color of his skin, but by his skill as an actor.

In order to become a professional actor, Ira Aldridge boarded a ship to London and became a Shakespearean actor in the early 1820s. He not only became the first black actor to play the role of Othello, he also played other roles such as Shylock in The Merchant of Venice, Gambia in The Slave, and other roles that denounced the evils of slavery:
Aldridge chose to play a lot of anti-slavery roles, including Othello, as well as the standard lead parts in the repertoire,” said Tony Howard, professor of English at Warwick University.

Not only did his performances call attention to the evils of slavery, they also challenged preconceived notions of what black people were capable of. As you can see in this reproduction of Mr. Aldridge’s 1851 tour advertisements, Ira Aldridge chose to bill himself as “The African Roscius,” a reference to an ancient Roman actor. His performances were heralded for his poise and dignity. The Leeds Times highlights “The passions he admirably portrayed in the human breast.”

No sooner did the Moor make his appearance, than I felt myself, I confess it, instantly subjugated, not by the terrible and menacing look of the hero, but by the naturalness, calm dignity, and by the stamp of power and force that he manifested.
Ira Aldridge

From 1820 to his death in 1867, Mr. Aldridge toured more than 250 theatres across Britain and Ireland, and more than 225 theatres in Europe. Though he had much more success in Europe, Mr. Aldridge still had to confront prejudices. According to ArtUK.org:
One scathing (and racist) review for The Times claimed that: ‘His figure is unlucky for the stage; he is baker-knee’d and narrow-chested; and owing to the shape of his lips it is utterly impossible for him to pronounce English in such a manner as to satisfy even the fastidious ears of the gallery.’
https://artuk.org/discover/stories/ira-aldridge-a-brief-visual-history-of-the-black-shakespearean-actor
Thus, Aldridge’s performances confronted and challenged racist views of whether or not a real black person could play Othello, subtly changing the hearts and minds of the European public, at a time when the question of slavery threatened to rip Europe, (and later the United States) apart.
Although Aldridge didn’t arrive in Britain with the sole purpose of promoting the abolitionist movement, his impressive skill, charisma and oratory capabilities inevitably swayed public opinion. He became known for directly addressing the audience about the injustices of slavery on the closing night of his play at a given theatre (Source: https://artuk.org/discover/stories/ira-aldridge-a-brief-visual-history-of-the-black-shakespearean-actor )
As I’ve written before, Shakespeare has a complicated relationship with the American Civil War, and ironically, many people in the Civil War were Shakespearean actors. More importantly, England at this time was deeply divided about whether or not to support the Union or the Confederacy. England was embroiled in the cotton trade with America, and thus had an economic incentive to support the South. At the same time, public opinion was very much against slavery at the time, and Aldridge helped keep England’s public within that mindset.

Ira Aldridge cared about abolitionism and making life better for black people, especially actors. Not only did he speak out against slavery onstage, he also helped change hearts and minds in local communities. According to ArtUK, in 1828, Mr. Aldridge was approached by Sir Skears Rew to become the new manager of the Coventry Theater. He was the first black man to manage an English theater. Aldridge became a beloved member of the community of Coventry and may have helped inspire the community to petition Parliament to abolish slavery. EThus, Mr. Aldridge’s success in Europe helped open doors for European black actors and encouraged the abolitionist movement, while his sympathetic portrayals of former slaves and oppressed peoples helped change hearts and minds.
“Aldridge has always interested black stars, but the wider influence he had is not well known,” said Howard. “Robeson was a great fan of his, and when he came to London to play Othello in 1930 at the Savoy, he put on an exhibition about Aldridge in respect of his memory.”
Vanessa Thorpe: “From 19th-century black pioneer to cultural ambassador of Coventry.” The Guardian, November 12th, 2016. https://www.theguardian.com/uk-news/2016/nov/13/black-theatre-ira-aldridge-coventry-slavery
For nearly 100 years, actors and devotees of Mr. Aldridge have been inspired by his life. As the quote above indicates, the next great American Shakespearean Paul Robeson helped build his career on Aldridge’s success; being the first black man to play Othello on the American stage, and eventually touring Europe himself as an actor and a distinguished opera singer. Click below to read more about how Aldridge inspired generations of black actors, and his tours helped bring Shakespeare to many previously unknown European countries.
https://www.shakespeare.org.uk/explore-shakespeare/blogs/legacy-ira-aldridge/
In modern films and plays, Mr. Aldridge is remembered as a hero, and rightfully so. In the play “Red Velvet,” actor Adrian Lester plays Aldridge and highlights his struggles and successful contributions to the theatre. He was not only a great actor but a dignified and courageous champion of the rights of all people. I’m proud to conclude my black history month posts with this review of the life and career of a man who inspires all Shakespeareans and turned his profession into a powerful call for change.
Stratford-upon-Avon’s first Black Othellos
https://www.folger.edu/blogs/shakespeare-and-beyond/ira-aldridge/
https://www.chicagoshakes.com/education/teaching_resources/teacher_handbooks/red_velvet/ira_aldridge

In this virtual version of my popular “Macbeth” course, you will engage with William Shakespeare himself and learn about his play in a fun, spooky, and interactive way!
Unlike my previous “Macbeth” course, all teacher interactions will be done through the use of pre-recorded video.
Through a combination of multimedia lectures, online games, and a digital escape room, students will delve into the plot, characters, and themes of “Macbeth.” The class is designed to be interactive, fun, smart, and spooky.
The class is organized into five parts using a combination of Nearpod, online games, videos, and a digital escape room.

You will play a video where William Shakespeare (played by me), will introduce the plot, characters, and literary terms in the play, “Macbeth,” The video will feature graphics, video, and recordings that will explain the plot and who the characters are, and their significance to the plot. Shakespeare will also take time to define a series of vocabulary terms like “soliloquy” and “tragic flaw,” terms that explain his unique writing style and how he constructed his tragedies.
After the video, students will participate in a group quiz via Nearpod. The quiz will cover the vocabulary words the students just learned, as well as the characters. and see their scores that will show how well they applied their knowledge from Part I.




Students will learn via Nearpod and Youtube about the English King James I, the monarch for whom Shakespeare wrote “Macbeth.” First, the students will read 1-3 slides with some historical details about the king. Then the students will watch a funny parody song about the life of the Stuart monarchs and answer questions about King James’ life. The section will conclude with slides and a virtual tour of Parliament about the infamous Gunpowder Plot, where an assassin tried to blow up the English government!


Using Nearpod, students will delve into the tragic history of the persecution of witches, which Shakespeare incorporated into “Macbeth.” The students will then read an article about the characters of the witches and answer open-ended questions on Nearpod. Next, the students will read an article about the alleged ‘Curse of Macbeth,’ and learn about the long-standing theater superstition. The class will conclude with an online game via Scratch, where you play as Macbeth and deliver the famous Dagger Speech before going to kill the king.
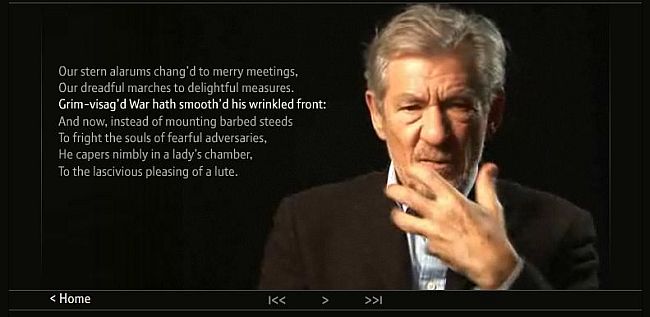

As you know, I’ve played Macbeth professionally and have written articles about the experience. Using Nearpod slides, online articles, and a Youtube video of Sir Ian McKellen, students will deconstruct the process of creating a Shakespearean character, and how actors make famous speeches fresh and alive.
Part V: The Digital Escape Room (Spoiler Free Version)
In a combination video/ website, Shakespeare will direct the students to a digital Escape Room, a game where students pretend that the witches from Macbeth have trapped them and Shakespeare in a cursed castle, and the only way to get out is to finish a series of puzzles that cover the characters and vocabulary they learned. The Escape Room will include word searches, decoding ciphers, a sinister forest, and a clever interpretation of the famous dagger speech. The video is designed so Shakespeare allows you to solve the problems independently, or with him guiding you through them. Each puzzle you solve, you enter in a Google Form, getting you one step closer to escaping the cursed castle.

Richard the Second: “Non sans Droit?” by Paul Rycik
The motto which I titled this post means “Not Without Right.” I chose it because it’s Shakespeare’s family motto, but also because in my view, Richard the Second is a play about the Divine right of kings; it asks whether kings are appointed by God, and if so, does that mean that they are free to do what they want, and whether or not they can be deposed. Today I want to examine how these questions are addressed in the play. I’ll do this by showing you passages from the text on video with a few notes by me. These recordings are by the Royal Shakespeare Company, England’s premiere acting troupe.
Picture #1- The Wilton Diptych
http://www.nationalgallery.org.uk/cgi-bin/WebObjects.dll/CollectionPublisher.woa/wa/work?workNumber=NG4451
This picture from the National Gallery in London illustrates admirably how Richard, who was the son of the Black Prince, the greatest warrior in English history, truly believed he was appointed by God. It depicts the 10 year-old king in full golden robes, being blessed by the Baby Jesus, the Virgin Mary, John the Baptist, Edward the Confessor, and St. Edmund. As I said before, Richard was only 10 when he was crowned; he believed he was God’s representative his whole life.
Video #1– Act IV, Scene I David Tennent playing Richard the Second
This is a recording of the famous Deposition Scene in which Richard must give his crown up to Henry Bolingbroke. It is clear from the text that Richard considers this not only treason but a form of blasphemy. This is evidenced in such passages where Richard compares himself to Jesus, another king betrayed by his followers.
“So Judas did to Christ, but he in 12 found truth in all but one, I in 12,00 none,”
Richard is in no doubt that he is appointed by God, and anyone who tries to question or depose him is damned.
Other characters take differing views on the divine right- the gardeners don’t believe in divine right- to them, a kingdom is ruled by men, not divine incarnations. They are pragmatic and think Richard’s claims foolish
Video #2 Act II, scene I- Patrick Stewart speaking as John of Gaunt
John of Gaunt believed in divine right, that’s why he killed Woodstock. In this famous speech, Gaunt reveals his passion for England, how he believes it has a special place among nations, and that a king’s duty is to protect it. But, when Richard sells land, Gaunt is forced to question how can a king be divine if his actions are wrong. He even suggests that Richard is no longer worthy of his royal blood: “O, spare me not, my brother Edward’s son; that blood already, like the pelican, hast thou tapped out and drunkenly caroused.”
Picture #2 Henry Bolingbroke from the 1975 production of Richard II
Bolingbroke’s motives are secret throughout the play. We don’t know if he always intended to seize the crown, whether he was forced to by his followers, or if he was forced to because Richard put him in an impossible position- his father’s lands seized by the crown and himself an exile. Equally enigmatic is if Bolingbroke believes in divine right. If he does, Bolingbroke must feel unimaginable guilt, especially in the scene when Richard is deposed. (Act IV, i) In the scene, Richard warns Bolingbroke that God will damn him for betraying his king, “The deposing of a king and cracking the strong warrant of an oath, marked with a blot, damned in the book of heaven.”
Once Richard is dead, Bolingbroke is forever shaken, paranoid, and fearful of assassination. My thinking is that Bolingbroke did believe that what he did was truly terrible and he spends the rest of his life mourning over it. This is why in the next play, Henry IV, Bolingbroke, now the king, says one of the most famous lines Shakespeare ever wrote: “Uneasy is the head that wears the crown.”
As you can see- there are several differing viewpoints on the issue of divine right- some people believe in it, some don’t. Thus the issue is never resolved because no one is proven right. I’ve written before that on controversial issues, Shakespeare never presents one view stronger than the other; he gives voice to every side of an issue and merely shows the conflict that happens when these characters fight with each other. It is up to the audience to choose sides.
Interesting Side note: The Deposition Scene I referred to earlier has a very disreputable history- it was considered anti-government because the censors claimed it favored the deposing of kings. One of the Queen’s favorite lords, the Earl of Essex ordered the scene played on February 7th, 1601 for that purpose. He planned to use it to rally the people and start an armed rebellion against the queen. Shakespeare’s entire company was arrested and interrogated as co-conspirators. Fortunately, they got away with it, as this document shows:
Document: Examination of Augustine Phillips, February 17, 1601

Shakespeare’s company claimed that the only reason they put on the play was that the lords offered more cash than the usual fee for performing at court. They got the government to buy their story, but, (as scholar Michael Wood claims), maybe the Queen wasn’t fooled- she asked them to perform the same play, right before Essex’s execution. When he died, she was reported as saying: “I am Richard the Second, know ye not that.”

If you liked this post, you might enjoy signing up for my course on Shakespeare’s History Plays on Outschool.com. Click the link below to sign up:
