Let me begin by admitting that this post was harder to write than my Christmas post because pre Christian traditions are harder to pin down. In addition, to give you my standard disclaimer, I don’t believe it’s really possible to definitively know how or if Shakespeare celebrated Halloween, but since the history of Halloween is long and fascinating, and since Shakespeare’s plays influenced that history, I feel it’s worth exploring.
Part I: Origins of Halloween
Almost every culture on Earth has a middle fall celebration that calls to mind the bounty of the harvest, and the inevitable approach of winter. Most of our Halloween traditions are based on the ancient European festival of Samhuin.
What is Samhuin?

Over 2,000 years ago, the Celts inhabited much of the British Isles. They believed in many gods and spirits that controlled nature and the seasons. To thank the gods for the harvest the Celts gave them offerings like apples, and threw parties to celebrate the gods’ bounty.
When the Romans conquered the Celts, they co-opted some of their religious practices. For instance the tradition of giving apples as offerings to the Roman goddess Pomona. This tradition of course, evolved into our modern Halloween tradition of bobbing for apples. Honoring the harvest also went hand in hand with darker traditions; ones inspired by fear of death, decay, and evil spirits.
With the Sun dying and the Earth growing cold in late October, cultures like the Celts and the Romans feared that evil fairies and ghosts could cross over into our world. In particular the Celts believed that around the night of October 31st, the veil between the living and the dead was the thinnest.
Samhuinn was a liminal time between our world and the Otherworld. It’s a night when the souls of dead loved ones as well as spirits and fairies – the aos sí in Irish mythology and aes sídhe or sìth in Scottish mythology – could come through to visit. Deceased family members were honoured with seats at the evening feast, and offerings of milk and baked goods were left at the front door for the Fairies.
At some point people decided to dress up as the spirits to ward them off, and this evolved into our modern day trick or treating.
These traditions did not die once England became Christian, (after it was conquered by the Romans), they simply translated into a different form. Halloween actually translates as “All Hallows Eve,” a Catholic celebration of of dressing up as pagan spirits and giving offerings of the harvest to honor Catholic saints as well as departed love ones.
Part II: What might Shakespeare have Done on Halloween?
Although Shakespeare never directly mentions Halloween, he lived in a world that kept many of these folk traditions alive. Shakespeare was the grandson of a farmer and his father was a devout Catholic, so he probably was brought up in these ancient Halloween traditions. He probably would have attended some kind of harvest festival to celebrate the bounty of the summer, and might have put food out for his departed family members.
Samhain is still heralded by the baking of kornigou, cakes baked in the shape of antlers to commemorate the god of winter shedding his ‘cuckold’ horns as he returns to his kingdom in the otherworld. On the Isle of Man in the Irish sea, the Manx celebrate Hop-tu-Naa, which is a celebration of the original New Year’s Eve and children dress as scary beings, carry turnips and go from home to home asking for sweets or money.
Source: https://theancientweb.com/2010/10/the-origins-of-halloween-part-1/
Call me a softie but I really like the idea of Shakespeare baking treats like soul cakes for neighborhood kids or telling scary stories about a bonfire. The kornigou is more commonly known as the Soul Cake, and it’s still popular today. It’s even been immortalized in song:
You can even make it yourself: www.cardamomdaysfood.com/recipe/soul-cakes/
Another tradition was dancing around ancient Celtic burial mounds. According to tradition, these mounds were home to spirits and Fairies, and could be portals to the land of the dead. In Irish folklore, poets and storytellers had the power to pass between these two realms. Maybe Shakespeare himself visited such a mound in his youth and was inspired to write about the fairy queen Titania and the hobgoblin Robin Goodfellow. Archeologists are still learning about these ancient ruins today (source: Smithson.com)
• Theater

The most tantalizing ancient Halloween tradition is mumming, a kind of amateur theater practiced by the ancient Celts. Like modern Sunday school plays the plays were a religious ritual designed goal to honor the gods and the harvest.
Mumming, a type of folk play, was used to tell traditional Samhuinn stories about battles or the winter goddess Cailleach (meaning “old hag”), who began winter by washing her hair in the whirlpool of Corryvreck.
For a modern example of this of these traditions you can look at the Edinburgh fire festival which preserves the kind of mumming that the Celts might have done on Samhuin and Shakespeare might have seen. It’s highly ritualistic, immersive, and the characters have spooky similarities to some of Shakespeare’s plays.
To give you an idea of how mumming might have influenced Shakespeare, watch this trailer for the 2017 Edinburgh Fire Festival:
• What you can see in the trailer:
1. Keening- the wild women screaming as a way to lament, honor, and guide the dead. Characters like Constance in King John have many similar qualities.
2. The fight between the Summer King and the Winter Lord. Many Celtic stories dramatize the change of seasons from summer to winter as a battle. Even the duel between King Arthur and his young son Mordred could be seen in this context. In another interesting interpretation, Jennifer Lee Carroll in her book Haunt Me Still, interprets this mummers play as a pagan retelling of the story of Macbeth.
3. You can see brightly colored figures some designed to honor the changing of the seasons, and wild, animalistic people, presumably playing the roles of the Fairies, goblins, or other creatures that appear on Samhuin. It’s not much of a stretch to see these figures as the Fairies of Midsummer Night’s Dream, or the witches of Macbeth.
Part III: What did Shakespeare mention about Halloween?

Ghosts appear in five of Shakespeare’s plays. We see reference to all kinds of Fairies, goblins, and spirits and even a couple times people dressing up to ward off evil. In Titus Andronicus, the queen of the Goths disguises herself and her sons as spirits of revenge and go to Titus’ house to torment him, and then the old man Titus tricking them into coming to his house, where he takes his revenge.

One Shakespeare play that I think perfectly encapsulates the Halloween traditions of the English countryside is Merry Wives Of Windsor, specifically the scene in which Falstaff is tormented by a ghost story.
In the play, the fat, drunk knight Sir John Falstaff has been trying to seduce two married women, Mistress Page and Mistress Ford. Page devises a plan to scare and humiliate Falstaff, by dressing up her husband as the terrifying ghost of Herne the Hunter:
• 4.4 MISTRESS PAGE
• There is an old tale goes that Herne the hunter,
Sometime a keeper here in Windsor forest,
Doth all the winter-time, at still midnight,
Walk round about an oak, with great ragg’d horns;
And there he blasts the tree and takes the cattle
And makes milch-kine yield blood and shakes a chain
In a most hideous and dreadful manner:
You have heard of such a spirit, and well you know
The superstitious idle-headed eld
Received and did deliver to our age
This tale of Herne the hunter for a truth.

Herne the Hunter is a real medieval legend about a man who was hanged for poaching deer in Windsor park and now haunts the forest with horns on his head. Not only does Master Ford dress as Herne, The witty housewives dress the neighborhood children like Fairies and instruct them to pinch the fat knight and burn him with lit candles. Essentially this scene is a Shakespearean trick or treating moment with a ghost story to boot. Plus as Mistress Page mentioned, the ghost haunts Windsor towards the the oncoming of Winter, so it’s not entirely unlikely that it would be that this scene was originally played around the time of Halloween.

How did Shakespeare contribute?

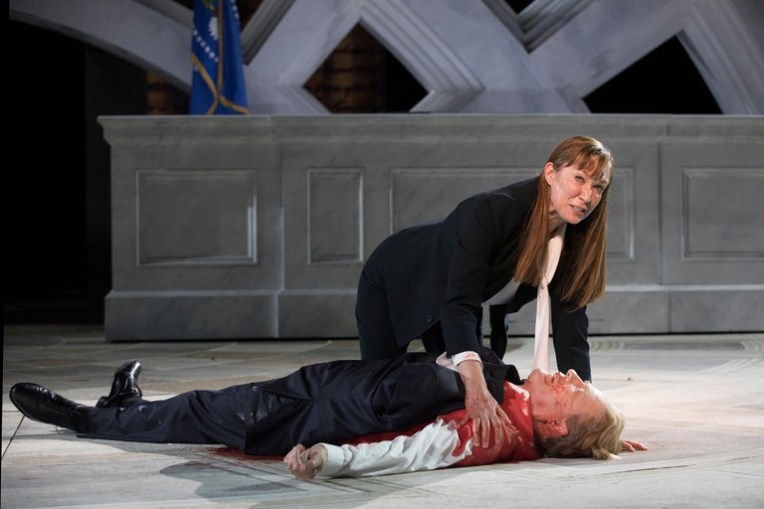
Scholars describe Shakespeare’s mind like a magpie, taking myths, legends, history, and books to come up with his own plays. As you have seen, the ancient traditions of Halloween had a powerful effect on Shakespeare’s plays. But, did he contribute to those traditions himself? I would say yes in a big way. First of all the image of Hamlet holding a skull has inspired many other Halloween images:

David Tennant in Hamlet, RSC 2008
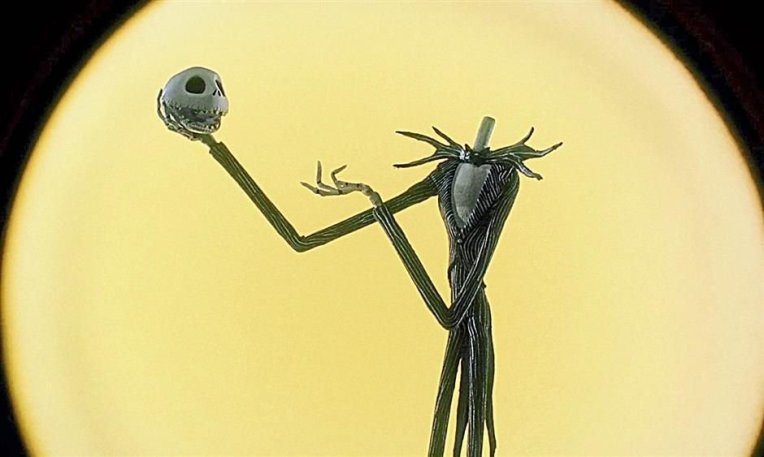

Jack Skellington in The Nightmare Before Christmas, 1993.
But I think Shakespeare’s greatest contribution to how we celebrate Halloween are centered within the witches of Macbeth.

Though Shakespeare by no means invented the concept of witchcraft, he did popularize the idea of the wicked witch, and helped form our modern view of what a witch is. The image he created in Macbeth
More than that, I would argue that the modern wicked witch would be all but silent without Shakespeare. When you think of what a witch might say, besides a series of high pitched cackling, what do you think of? Probably you think of this:

Or this:

Shakespeare’s bizarre and cryptic language helped inspire countless other interpretations of witches, and thus, a way for audiences to deal with the temptations that lurk in our hearts.




In conclusion, we don’t know how Shakespeare celebrated Halloween or even if he did to begin with; Halloween and Shakespeare’s life are both frought with mystery and legend, but one thing is dead certain; Halloween would not be the same without him. He absorbed the ancient rituals of the Celts and Romans and crafted some modern Halloween ideas and images that endure to this day.
Sources
https://www.historic-uk.com/CultureUK/Halloween/
https://www.bbc.co.uk/newsround/15169373
Thanks very much for reading! If you liked this post, please consider signing up for my new “Macbeth” online class via Outschool.com. One really fun part of the class will be an escape room where you use your knowledge of Macbeth to escape a cursed castle:


















 Ever since this 1906 book of the plants mentioned in Shakespeare’s plays, great cities and private garden groups have created gardens that honor the fertile imagination of The Bard Of Avon. There are 33 of these Shakespeare gardens worldwide, in cities like New York, Barcelona, and of course, Shakespeare’s home town of Stratford Upon Avon.
Ever since this 1906 book of the plants mentioned in Shakespeare’s plays, great cities and private garden groups have created gardens that honor the fertile imagination of The Bard Of Avon. There are 33 of these Shakespeare gardens worldwide, in cities like New York, Barcelona, and of course, Shakespeare’s home town of Stratford Upon Avon.








































