Course Description
- Concept: To explore the plot, characters, and themes of Shakespeare’s Julius Caesar while also gaining an insight into Ancient Roman history and culture.
- Student Description: Delve into the passionate speeches of Brutus and Antony in Shakespeare’s Julius Caesar, which led a whole country to revolution.
- Parent Description Using self-paced online activities, and a helpful handout, your child(ren) will analyze the rhetoric and persuasive power in two speeches from Shakespeare’s “Julius Caesar.” The course will also cover the culture of Ancient Rome, and the circumstances that led to Julius Caesar’s assasination, which inadvertently led to the birth of the Roman Empire.
- Course Organizaiton (the class is divided into 4 parts that students can complete at their own pace over a week-long period
- Each lesson will have:
- “That Is the Question” (Essential Question)
- Lesson Objectives
- Set the Scene (Background and context)- 1-3 slides
- The Players (biography) 1-3 slides
- Go Deeper (Webquest)
- Explore military life and the lives of women in Rome using my blog and other websites as a guide.
- Post 3 things you learned to the Outschool page or send a photo of your completed handout.
- Words, Words Words (Vocabulary, famous lines)
- A Taste of Your Quality (Independant Project)
- Show us your mettle (Test)
- So each class should be 14-15 slides long.
- Each lesson will have:
Outline
Class I- Background on Caesar and Roman Culture

- That is the Question:
Why did Brutus feel Julius Caesar had to die?What was the aftermath?Can one person’s speech effect an entire nation?
- Lesson Objectives
To provide historical and political context to explain why Julius Caesar was assassinated, and how his death inadvertantly created the Roman Empire.To explain the Rhetorical Triangle, the building blocks of persuasive speech.To go through the story of Julius Caesar focusing on the effect of the speeches.To study the famous “Friends, Romans Countrymen” speech.To contrast this speech with some more recent political speeches and you think critically about:What does the speaker want?What tactics does he use?How effective is it?
- Set the Scene
- History
- Government
- Horrible History
- Military
- Government
- Culture
- Fashion: https://shakespeareanstudent.com/2022/03/11/the-fashion-is-the-fashion-ancient-roman-fashion-and-beauty/
- Role of Women: https://shakespeareanstudent.com/2021/03/29/i-lift-the-veil-on-shakespeares-celebrated-roman-female-characters-and-discuss-the-social-norms-they-embodied-and-challenged/
- The Lupercal- https://wordpress.com/post/shakespeareanstudent.com/4545
- History
- The Players (slides)
- Julius Caesar Julius Caesar – Greatest Conqueror Ever?
- Cassius Longinus
- Marcus Brutus
- Marc Antony
- Go Deeper-
- Go to Google Arts and Culture and find 3 facts and 3 pictures of Caesar
- Answer the following Questions:
- Name 3 jobs Caesar had in the Roman Republic
- Was Caesar Deaf? Was he epileptic?
- Name 3 things Caesar accomplished during his career.
Go to opensourceshakespeare.com and look at Caesar’s lines- how does Caesar view himself? Write 3 examples.
- Words Words Words
- Republic
- Dictator
- Lupercal
- Assassinate
- Senate
- A Taste Of Your Quality
- Make a news headline about Caesar’s triumph. How would you report on it? Would you be allowed to say anything bad about Caesar?
- Show Us Your Mettle
- Quizlet for the terms
Class 2- Cassius Manipulates Brutus

That Is the Question-
How does Cassius convince his brother-in-law Brutus to betray and assassinate Caesar, his friend and colleague?
Learning Objectives-
- To give historical context as to why the Senate in general, (and Cassius in particular), feared and hated Caesar.
- To examine Brutus’ character
- To demonstrate how Cassius uses persuasive speech
Setting the Scene- The Plot
The Players-
Cassius- slide/ https://www.rsc.org.uk/shakespeare-learning-zone/julius-caesar/character/whos-who
Write 3 facts we learn about Cassius at the start of the play:
Brutus:
https://www.rsc.org.uk/shakespeare-learning-zone/julius-caesar/character/whos-who
Go Deeper-
Brutus- Podcast episode. I posit in this episode that Brutus is
Words, Words, Words-
- Traitor
- Republic
- Dictator
- Revolution
- Ethos
- Pathos
- Logos
- Rhetoric
- Colossus
- Aeneus
A Taste Of Your Quality:
(Independent work): We’ll examine a painting of Brutus’ ancestor Lucius and learn why Brutus values Rome more than even family.
Show Us Your Mettle:
Quizzes on Brutus
Class 3- Antony and Brutus’ Dueling Speeches
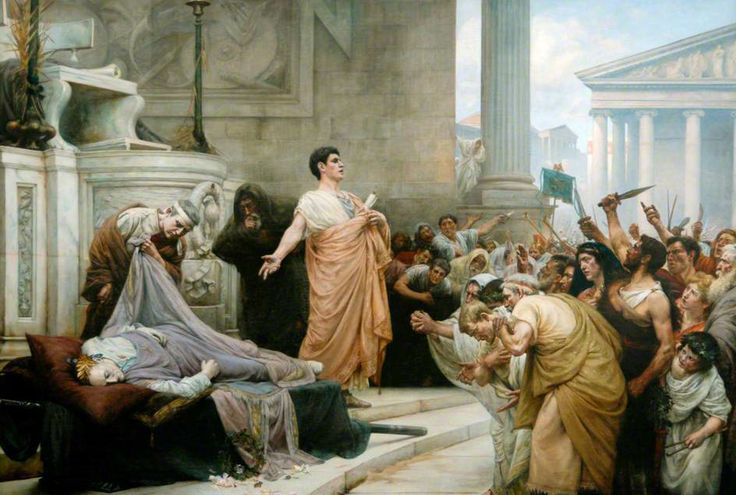

That Is the Question
- After Caesar’s Death, his friend Marc Antony held a funeral for him where he gives the famous “Friends, Romans, Countrymen” speech. How did Antony’s speech affect the crowd?
- Brutus has a speech where he explains why he killed Caesar. What does he say, and how effectively does he say it?
- Antony was secretly plotting to take power for himself, and get Brutus and Cassius killed. How did he do it?
- Do speeches have the power to change a nation?
Learning Objectives
- To explain the Rhetorical Triangle, the building blocks of persuasive speech.
- To study the famous “Friends, Romans Countrymen” speech, as well
- To look at these speeches and get you to think critically about:
- What does the speaker want?
- What tactics does he use?
- How effective is it?
Setting the Scene
RSC Learning Zone- Act III, Scene 2 https://www.rsc.org.uk/shakespeare-learning-zone/julius-caesar/story/scene-by-scene
The Players (use the videos from the RSC)
Brutus- Man of Honour VS Man of Action | Julius Caesar | Royal Shakespeare Company
Antony Julius Caesar, Act 3 Scene 2 | 2012 | Royal Shakespeare Company
Go Deeper
- Go to my blog post and learn about the terms for rhetorical devices:
- https://shakespeareanstudent.com/2018/04/21/close-reading-friends-romans-countrymen/
Words, Words, Words
- Irony
- Antimetabole
- Rhetoric
- Countrymen
- Lend
- Interred
- Noble
- Hath
- Grievous
- Coffer
- Honorable
- Lupercal
- Cause
- Mourn
A Taste Of Your Quality
- Watch the video of Antony’s speech:
- fill out the handout:
- Write 2-3 sentences about Marc Antony’s speech about what he was trying to
- get the crowd to do and how he used rhetoric to do it.
- Use at least 2 quotes and identify whether they use Ethos, Pathos, or Logos
- https://myshakespeare.com/julius-caesar/act-3-scene-2
- https://www.bardweb.net/content/readings/caesar/lines.html
Quizzes
Class 4- After Caesar-

We’ll talk about the consequences of violent revolutions and how Julius Caesar has inspired some of the greatest speeches in political history.
-Patrick Henry
– Gettysburg Address
– Mean Girls
That Is the Question
- How have people interpreted the play “Julius Caesar” in America?
- Does this play promote violence?
- What kind of violent speech do we deal with in politics today?
Learning Objectives
- To show the link between American History and Julius Caesar
- To address the controversy and the misconception that the play promotes violent assassination.
- To end on a cautionary note people must think critically about what they hear in politics and not make rash decisions based on appeals to fear.
Setting the Scene- US History
- America was founded using the principles of republican government that Ancient Rome used- with a senate, and a series of checks and balances to ensure no one has too much power.
- America was founded in a violent revolution, and some of our country’s early leaders used Brutus as an inspiration- to overcome a tyrannical king.
- In later years, however, some people have forgotten what happened to Brutus
- Today, we are often bombarded with speech that encourages fear and anger and we must think critically when we hear such speech in whatever forum- Roman, or Reddit.
The Players (use my JC lecture?)
- Patrick Henry
- Abraham Lincoln
- John Wilkes Booth
- Donald Trump
Go Deeper
-Watch the Caesar Video
– How does the play promote nonviolence?
– How did Brutus’ assassination fail to save the Roman Republic?
Words, Words, Words
Four-score
Dedicate
proposition
Civil War
Endure
Consecrate
Devotion
A Taste Of Your Quality (Night Cafe)
- Use AI to create your own image for Julius Caesar
- What time and place would you set the play in?
- how do you see him- is he a hero, or a tyrant?