Happy Ides of March every one. I hope you have enjoyed all the posts for my Roman week. If I have time, I will try to post a few more, since I have not touched on Cymbaline or Titus Andronicus.This will not be an in depth character analysis. I won’t go into every scene and speech of Brutus’. My goal is to look at the history and the actions of Brutus in the play to show why he is such an amazing and ambigous character.

Marcus Brutus was born in 85 BC. Shakespeare’s source for the play, Plutarch’s lives of the Noble Greeks and Romans, mentions that his desire to kill Caesar might have been tied to his family: Brutus’ ancestor was Lucius Junius Brutus, the man who drove out the last king of Rome, and first consul. Below is the famous painting of Lucius foiling a plot to restore the monarchy, but to do so, he had to sentence his own sons to death:

Jaques Louis David, The Lictors Bring to Brutus the Bodies of His Sons, 1789.
https://www.khanacademy.org/humanities/monarchy-enlightenment/neo-classicism/v/david-the-lictors-returning-to-brutus-the-bodies-of-his-sons-1789
This was how seriously the Brutus family took defending the Roman Republic, they valued it even beyond their own family.
Brutus’ mother was Servilia, half sister of Caesar’s longtime critic, the senator Cato. He even married Cato’s daughter Portia! So you can see that once Caesar starts acting like a king, Brutus must have felt a tremendous amount of pressure from his Family to stay true to his Republican ideology. On the other hand, Servillia was actually Caesar’s mistress and Brutus owed his life to Caesar. After Brutus fought against Casesar, they reconciled after the Battle of Pharsalus in 48 BC:
Most of those who were taken alive Caesar incorporated in his legions, and to many men of prominence he granted immunity. One of these was Brutus, who afterwards slew him. Caesar was distressed, we are told, when Brutus was not to be found, but when he was brought into his presence safe and sound, was pleased beyond measure- Plutarch, retrieved from: http://penelope.uchicago.edu/Thayer/E/Roman/Texts/Plutarch/Lives/Caesar*.html
Despite his close ties to Caesar, Brutus chose to betray and assassinate him, so the question remains, why?

In the play and in Plutarch, Brutus is persuaded by Cassius Longinus, his brother in law and colleague in the Roman Senate. As you remember from my post on “Friends, Romans, Countrymen,” there are three basic kinds of persuasive speech, and Cassius uses all three:

1. Ethos “If you do know that I do fawn on men, and hold them hard, and after scandal them… then hold me dangerous.”
2. Logos- Cassius points out a series of embarrassing stories about Caesar that set up the following argument:
• Caesar is weak and frail
• Gods cannot be frail
• Why is Caesar treated like a god?
3. Pathos
• The people
• Fear of tyranny
• Brutus’ family honor- this is the real knife that kills any doubt Brutus had. Cassius reminds Brutus of his ancestor Lucius and how he would rather die than see a king in Rome again.
The soliloquy
Brutus. It must be by his death: and for my part,
I know no personal cause to spurn at him,
But for the general. He would be crown’d:
How that might change his nature, there’s the question.
It is the bright day that brings forth the adder;
And that craves wary walking. Crown him?—that;—
And then, I grant, we put a sting in him,
That at his will he may do danger with.
The abuse of greatness is, when it disjoins
Remorse from power: and, to speak truth of Caesar,
I have not known when his affections sway’d
More than his reason. But ’tis a common proof,
That lowliness is young ambition’s ladder,
Whereto the climber-upward turns his face;
But when he once attains the upmost round.
He then unto the ladder turns his back,
Looks in the clouds, scorning the base degrees
By which he did ascend. So Caesar may.
Then, lest he may, prevent. And, since the quarrel
Will bear no colour for the thing he is,
Fashion it thus; that what he is, augmented,
Would run to these and these extremities:
And therefore think him as a serpent’s egg
Which, hatch’d, would, as his kind, grow mischievous,
And kill him in the shell.
• This speech is a direct predecessor for “To be or not to be,” and Macbeth’s “If it were done,” soliloquy. https://youtu.be/IoDwXjKIenI
- All three speakers are talking about murder and can’t bring themselves to say either the word murder, nor mention the name of the man who will die.
• All references to murder are in passive voice, as if Brutus wishes a lightning bolt would kill Caesar, so he doesn’t have to accept the responsibility of killing.
•Compared to Hamlet and Macbeth, Brutus’ text is flat, The speech depends on the actor to show the torment in his soul.
- One question that the actor must answer for himself is, is Brutus really concerned for the well being of Rome, or does he want Caesar dead for another reason?
After the soliloquy, Brutus throws himself into the role of head conspirator: https://youtu.be/ibzqdoV-BcU https://youtu.be/ibzqdoV-BcU
You can see in this video that Brutus speaks eloquently about how just the cause is and how only Caesar will die. This illustrates that Brutus is well spoken but not pragmatic. As we all know, Marc Anthony eventually gets the crowd to turn on Brutus and will become part of the army that hunts him and Cassius down. The dramatic irony is what helps the argument that Brutus is the real tragic hero of this play.
The murder and its aftermath

The rest as they say, is history. On March 15th, 44 BC, Brutus and the conspirators stabbed Caesar 17 times. In the play, before Caesar dies, he utters the famous line, “Et tu, Brute? Then fall Caesar!”
The line stands out because it is the only time anyone in this Roman play speaks in Latin. Now, I have heard a compelling argument from Professor J. Rufus Fears, that this might actually be a misquote, and what Caesar really said will amaze you. As I have mentioned, Brutus’ mother was Caesar’s mistress and the two of them were very close. At the time of Caesar’s death he was 40, while Caesar was 16 years his senior. Why did Caesar forgive Brutus fighing against him? Is it not possible that what he actually said was: “Et tu, son?” That’s a question for directors and actors, but it does heighten Brutus’ emotional conflic. Much like his ancestor Lucius, Marcus Brutus is caught between his ideals and his family.

During the funeral, Brutus has a very well crafted speech where he lays out his reasons for killing Caesar. He sets himself up as the friend of Rome. This video from the Royal Shakespeare Company explores the techniques that Brutus uses to get the crowd on his side: https://youtu.be/nyPlvuv8SSk
After Antony makes his speech however, the mob burns Brutus’ house and even slaughters a man just because he shares a name with one of the conspirators. Brutus and Cassius take their armies and flee Rome, and prepare to take on Antony and Octavian. The adversity Cassius and Brutus go through pushes them together and they behave like brothers; they fight and reconcile constantly: https://youtu.be/K9EAxjVC22M
In a way, these men are two sides of the same coin: Cassius is fiery but pragmatic while Brutus is stoic and idealistic. It’s like a tragedy in and of itself that these men weren’t melded into one man with Brutus’ heart and Cassius’ mind.
Is Brutus A Traitor?
Unlike Macbeth, Shakespeare’s text leaves it ambiguous as to whether Brutus was right or wrong to kill Caesar. Even Antony, who leads an army against him, ends the play by calling Brutus “The noblest Roman of them all.” Shakespeare also gives us few clues to Brutus’ motivations other than the speech I quoted earlier. Mainly we have to go on Brutus’ actions and their consequences.

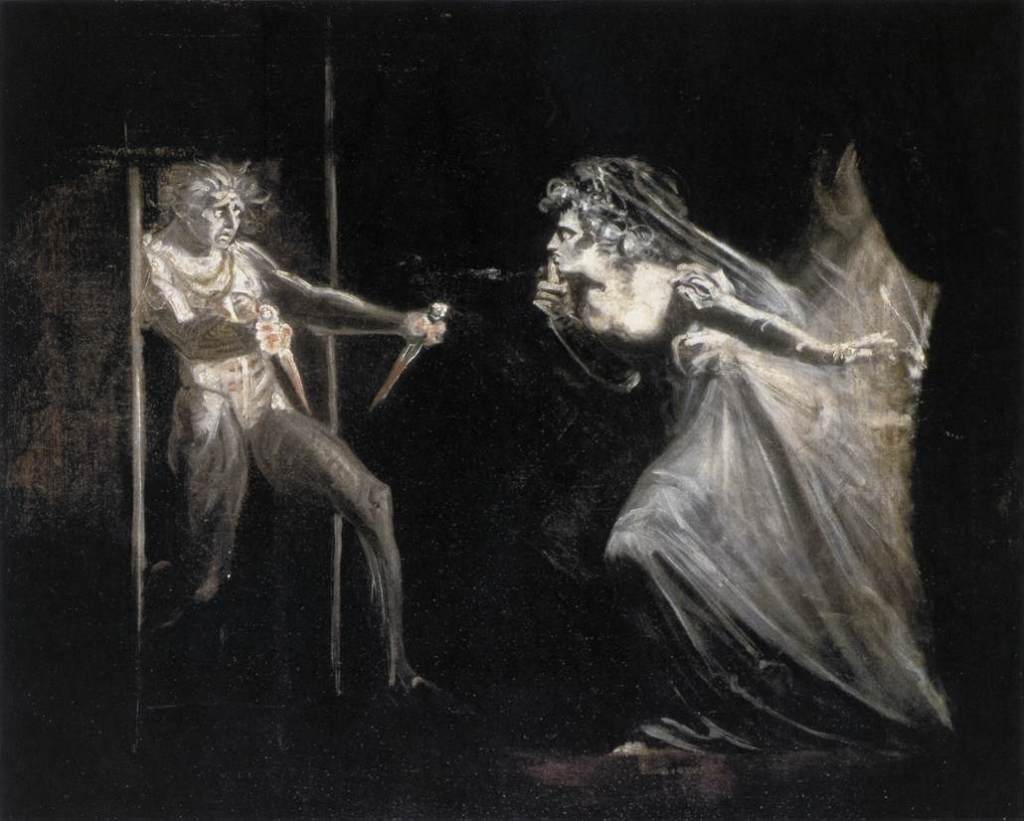
One moment that I think perfectly encapsulates the ambiguity of Brutus’ actions is the moment where he’s visited by Caesar’s ghost. In other tragedies like Macbeth and Richard III, the villain is tormented by the ghost or ghosts of people he murdered. The ghost serves as a manifestation of the murderer’s guilty conscience and torments him before his death. When Brutus sees Caesar, he does not follow this trope. He isn’t horrified, not struck by guilt, in fact, he wishes that the ghost would stay longer.
In Act 4, why does Caesar’s ghost appear? I don’t understand why Caesar’s ghost shows up. I dont understand the significance of that scene.
Expert Answers info
Shakespeare, as other Elizabethan writers, uses the idea of ghosts in his plays usually as a foreshadowing of events to come. In “Hamlet,” Hamlet has to deal with working out what to do with his father’s request for revenge, and also, whether the ghost is indeed his father. In “Macbeth“, Macbeth has to deal with the Ghost of Banquo showing up to dinner, literally haunting him. In “Richard III“, Richard deals with the ghosts of the men he has wronged right at the start of the play.
This haunting is significant also in “Julius Caesar“. The Ghost of Julius arrives on the eve of battle to literally haunt Brutus. Brutus had hoped that by killing Caesar he would enact change in Rome, however, the Roman Empire goes on, as does the reign of Caesar (albeit, a new Caesar).
As Brutus goes into battle, and the battle doesn’t go his way, he again turns to Julius Caesar, blaming him for the outcome of the battle,
O Julius Caesar, thou art mighty yet!
Thy spirit walks abroad, and turns our swords
In our own proper entrails. (5.3.94–96)
Shakespeare’s ghosts are visible to one person (as well as the audience, clearly) so those who react to the ghost are the ones who are supposed to learn from the arrival of the ghost, heeding the message from beyond the grave.
Enter the Ghost of CAESAR
How ill this taper burns! Ha! who comes here?
I think it is the weakness of mine eyes
That shapes this monstrous apparition.
It comes upon me. Art thou any thing?
Art thou some god, some angel, or some devil,
That makest my blood cold and my hair to stare?
Speak to me what thou art.
GHOST
Thy evil spirit, Brutus.
BRUTUS
Why comest thou?
GHOST
To tell thee thou shalt see me at Philippi.
BRUTUS
Well; then I shall see thee again?
GHOST
Ay, at Philippi.
BRUTUS
Why, I will see thee at Philippi, then.
Exit Ghost
Now I have taken heart thou vanishest.
Ill spirit, I would hold more talk with thee.
The ghost itself also resists the clearcut definition as a sign of a guilty conscience. It doesn’t accuse Brutus of murder, it doesn’t curse in fact, all the ghost says is that Brutus will see him at Philippi. Unlike Richard III or Macbeth, the ghost utters no curses or scare Brutus out of his mind.
The only conclusion that Brutus gleans is that his end is near. According to Dr. John Langdon, many Elizabethan ghosts serve as a shorthand to indicate that the play’s denouement is on its way. Brutus seems aware of this as well- he knows that if he sees a ghost, he’s likely to be one soon. Yet the reality of his impending death doesnt change Brutus; he doesn’t express remorse like Richard III or hopelessness like Macbeth, if anything his stocism and seeming world weariness makes him seem more like a hero like Hamlet during his “Not a whit, we defy augery,” speech. This passive embrace of fate is at the core Brutus and it illustrates how hard it is to truly decide if he is a villain or a hero.
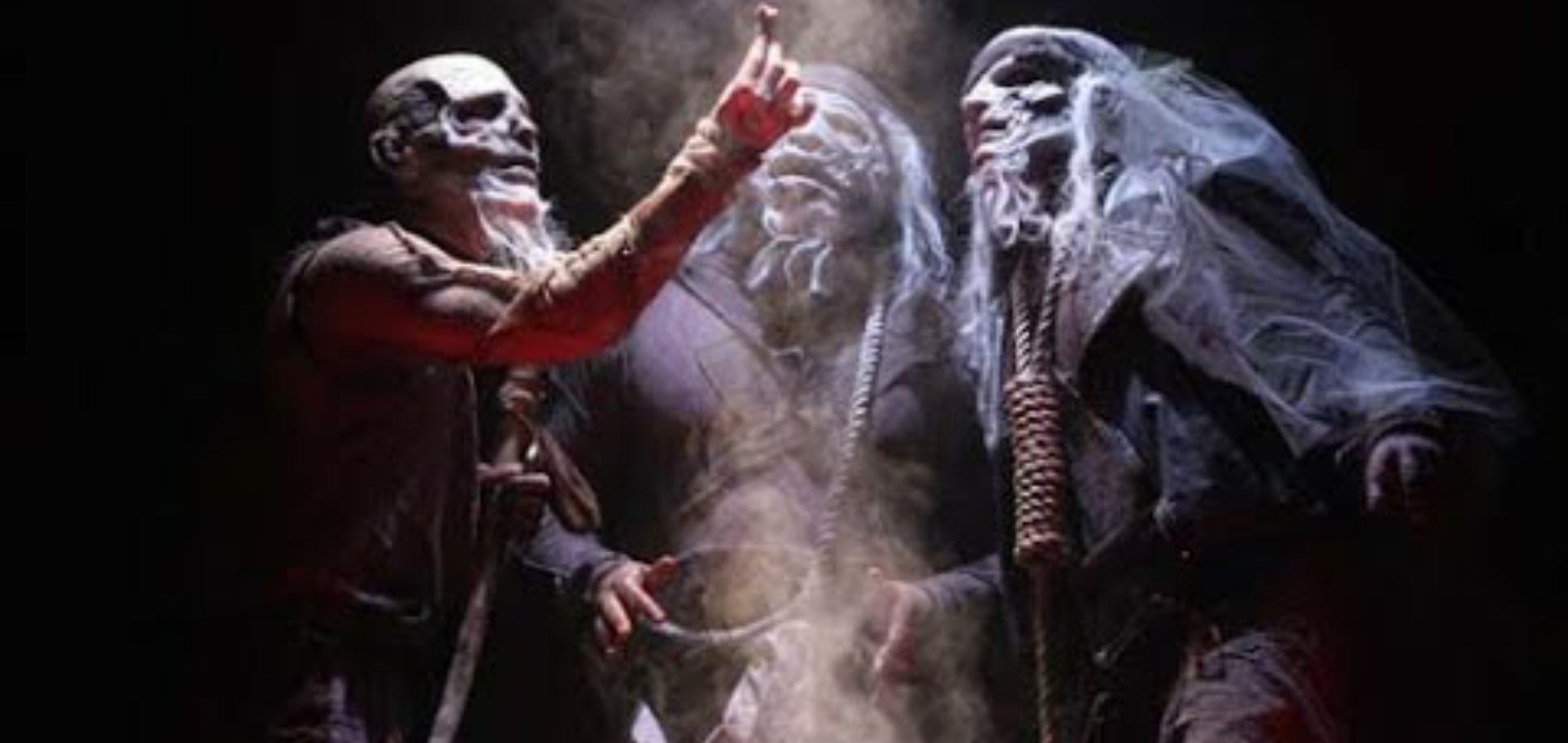
Though Shakespeare wrote the character of Brutus as ambiguous, over the centuries many artists and cultures have passed judgment on Brutus. Dante in his book Inferno example places Brutus and Cassius in the lowest circle of Hell, who along with Judas Iscariot, are being forever devoured by Satan himself, imagined below in a medieval illustration as a three-headed beast. You can see the name Brut in the head on the right.

By contrast, during the French Revolution, many statesmen referred to Brutus as a hero for his noble attempt to destroy a corrupt monarchy.
“One day men will be astonished by the fact that humanity in the eighteenth century was less advanced than in the time of Caesar. Then a tyrant was slain in the midst of the Senate with no formalities but thirty blows of a dagger and with no other law save the liberty of Rome” Louis Antoine de Saint-Just, November 13th, 1792, (2 months before the execution of Louis XVI).

As I have written before, in the 20th and 21st centuries, America has a somewhat more complex relationship with the character of Brutus. On the one hand, America was founded on the principle of resisting tyranny; it’s even on the state flag of Virginia, which is why some early productions of the play make Brutus a hero. On the other hand, as you see above, rebels and traitors like John Wilkes Booth have also taken inspiration from Brutus. His father and brother’s middle name was Brutus and all three brothers performed in the play one year before John turned theater performance into American tragedy.
Like Brutus, Booth seemed amazed with the world’s reaction to his deed, for after he assassinated the president, he wrote this in his journal:
[W]ith every man’s hand against me, I am here in despair. And why; For doing what Brutus was honored for … And yet I for striking down a greater tyrant than they ever knew am looked upon as a common cutthroat.”
John Wilkes Booth, April 21, 1865.
The most recent controversy over Brutus’ actions is the 2017 Shakespeare in the Park production of Caesar directed by Oscar Eustis. As I wrote before, when portraying Caesar as an American president, it tends to anger the political party of his supporters, but the play shows how unplanned political violence can destabilize a country. In these productions, Brutus seems a bit of a well meaning dupe or an naive patsy acting out of fear. On the other hand in cultures that have suffered many violent uprisings, Brutus is a figure that is all to common in places like Uganda, Iran, and the Taliban controlled world: https://youtu.be/5HU8SA33j2w
Brutus is a great character because Shakespeare keeps enough of his motives in the dark to allow for new interpretations, but also showing a man with relatable desires and fears get swept up in a dangerous and unpredictable time.