“She’s got…it, hasn’t she? The pestilence?” (O’Farrell, 105).
As this quote, (and the subtitle) suggests, Maggie O’Farrell’s novel Hamnet: A Novel About the Plague, focuses on the terror surrounding the plague and its devastating consequences on families. I really respect this book for its historical authenticity, it’s clever prose, and O’Farrell’s command of style, but I should warn you that this novel is definitely not for breezy summer reading.
If you are looking for a novel about William Shakespeare, this isn’t it; the Bard only appears in flashbacks. The action mainly concerns his wife and children. While Will was living and working in London for most of the year, his family lived in Stratford Upon Avon, along with the playwright’s mother and father. The novel has follows the characters across two times: 1582, when Shakespeare and his wife first met, courted and married, and around 1595, during an outbreak of plague that would (Spoiler Alert) eventually claim the life of Shakespeare’s son, Hamnet.


The novel has a very dour tone, but that is by design. The author herself writes that the premise of the book was to create a realistic (albeit fictional) account of the Shakespeare family as their only son fell sick and died.

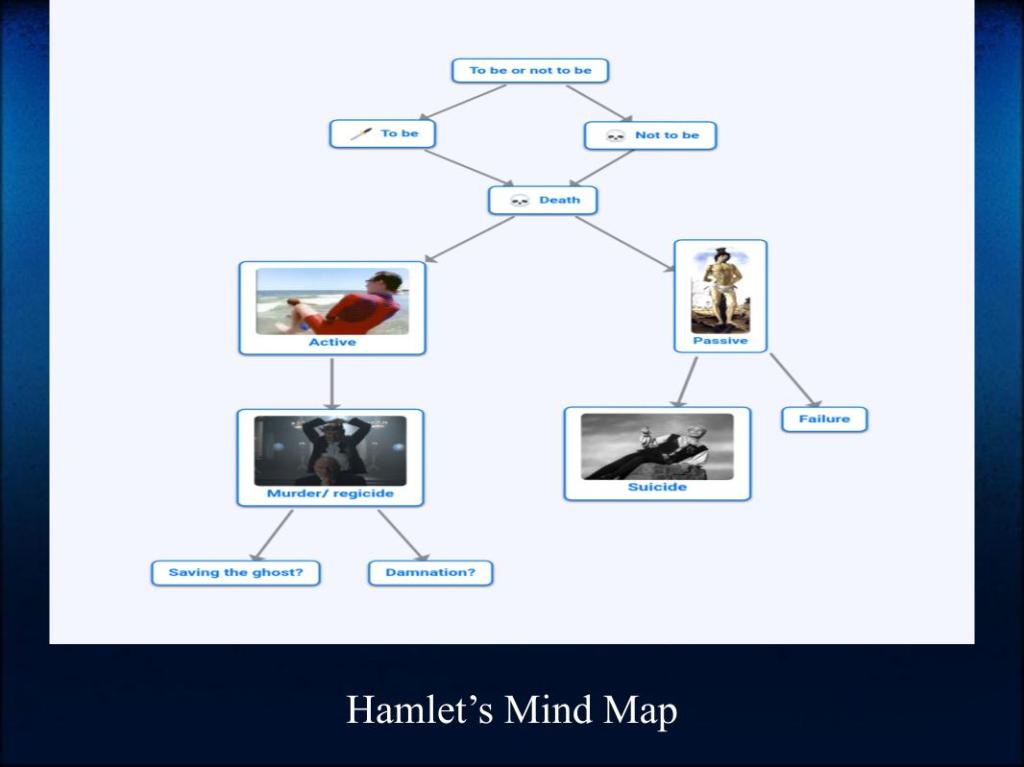
The premise is intriguing from a historical point of view. We have no diaries or correspondence that express how the Shakespeares dealt with this catastrophic loss, but many scholars believe that Shakespeare’s play Hamlet was a direct homage to his son, since in Elizabethan England the names Hamlet and Hamnet were used interchangeably. Still, it must have effected Will in other ways, and it had to have had an effect on Hamnet’s mother and sisters, and that was O’Farrell’s focus when adapting this story as a novel.
I would describe the novel’s tone as ‘haunting,’ which is appropriate since it’s based around how a child’s death effected his family. It reminds me of a passage Shakespeare himself wrote about the death of a young boy in his play King John:
Grief fills the room up of my absent child,
Lies in his bed, walks up and down with me,
Puts on his pretty looks, repeats his words,
Remembers me of all his gracious parts,
Stuffs out his vacant garments with his form;
Then, have I reason to be fond of grief?
Fare you well: had you such a loss as I,
I could give better comfort than you do.
I will not keep this form upon my head,
When there is such disorder in my wit.
O Lord! my boy, my Arthur, my fair son!
My life, my joy, my food, my all the world!
My widow-comfort, and my sorrows' cure! King John Act III, Scene iv.
Like Constance in the quote above,, All the characters in Hamnet are haunted.
[Hamnet is pursued by plague. Will Shakespeare and Anne Hathaway are haunted by their abusive parents. Will’s father John by the loss of his business and social standing, and of course, everyone is haunted by Hamnet’s death.


Although the novel is mainly about Hamnet’s decline and death, my favorite parts of the book are flashbacks to the courtship and marriage of Will Shakespeare and Anne Hathaway. We know nothing about their real courtship, so O’Farrell borrows the plot from Shakespeare’s Taming Of the Shrew. Like Lucentio in Shrew,
The 18 year old William Shakespeare is a Latin tutor, (having not yet become a writer), who woos a misunderstood woman whom the town calls a shrew. In the book, Anne Hathaway is known as Agnes and (like many unmarried women of the period), is looked on as odd and somewhat wild. Many single women of this period would likely face discrimination, and sometimes. In this video, you can see how cunning women like Anne had an uneasy relationship with the local community; some saw them as an asset to the community, but others believed their abilities came from The Devil. For more information on Anne’s life, click here.
Anne is further isolated because of her strange abilities- in the book she owns a falcon, not a ladylike hobby for 1580s England. She is also skilled with medicinal plants and knows how to read palms. In essence, though the town ostracizes Anne, Shakespeare admires her cleverness, and the book implies that Shakespeare would later use her skills in characters like Kate from Shrew, Friar Lawrence (the skilled potion master), and maybe even the witches from Macbeth.
The reusing of Shakespeare’s plots doesn’t stop there- Before Anne and Will get married they are handfasted- that is they make a mutual promise to get married in front of witnesses. Anne knows that her family will not consent to their marriage given Shakespeare’s low economic prospects, so she convinces Will to get her pregnant. This mirrors Claudio and Juliet in Shakespeare’s Measure For Measure, who are publicly shamed and arrested for fornication, even though their only crime was not waiting until they had given a dowry to the groom’s parents before consumating the marriage.
One final master stroke of O’Farrel’s historical fictive tapestry is how she engineers the father son conflict between Will Shakespeare and his father John. Shakespeare loves to explore the power dynamic between boys on the cusp of manhood, and their already powerful fathers. In the case of John Shakespeare, O’ Farrell depicts him as a man who has worked, schemed, scammed, and clawed his way to the highest wealth his birth can allow him, but is now falling from grace, who has nothing but contempt for his son who seems like a worthless dreamer, incapable of hard work. This most closely echoes Shakespeare’s Prince Hal and King Henry, a son who must prove his fitness to be king to his father and to his nation. Watch this exchange from “The Hollow Crown” where the sick and aging John of Gaunt (Patrick Stuart), chastises his weak, effeminate nephew, King Richard II:
Historical Notes:
Infant mortality in Elizabethan England:
Even before Hamnet is born, his mother and mother in law are painfully aware that he might die young. Sadly this is very historically accurate. Infant mortality rates were high in Elizabethan England. According to Ian Mortimer in his book The Time Traveler’s Guide To Elizabethan England, mothers had to keep their children at arms length and not get too attached. Being a mother in this time meant dealing with the constant knowledge that your child might not survive:
In Stratford in the 1560s, there are on average, sixty-three children baptized every year- and forty-three children buried.
Mortimer, 27.
John Shakespeare’s fall John Shakespeare was more than a glover- he held a position in the Stratford Guild Hall- basically a city council position. He was in charge of hiring constables, keeping the peace, overseeing the brewing of ale, and approving theatrical entertainments for civic events. Probably John got his son interested in theater by letting him tag along to the sort of private performances he would have watched to determine whether a play or troupe was good enough for, for instance, the visit of a peer. However, by the 1580s, John was losing his business and selling off his land assets. Scholars suspect that either John was a closet Catholic, forced to pay fines every time he failed to attend protestant church, or he was avoiding church and his alderman council meetings because he knew his creditors would be there. In any case, O Farell takes this historical tidbit and turns John Shakespeare into a bitter, broken, abusive man whom Shakespeare can’t wait to get away from. Shakespeare and his wife bond over their abusive parents and dream of succeeding financially so they can get away from their parent’s influence.
Malt and wool The novel hints at John Shakespeare’s secret side business selling wool and malt, but never explicitly states that this practice was illegal. All wool was controlled by the Elizabethan government so it was illegal to sell it without special permission, and in 1570, John Shakespeare was caught selling wool illegally. He was also found guilty of money-lending, hoarding grain, and selling malt. This is why he tells his son to forget the wool he saw in the attic.


Historical Events Mentioned in Hamnet
- 1556 Anne Hathaway born. She’s referred to as Agnes in other court documents. Her father Richard owned a sheep farm in Hewland. At some point, her mother died and her father Richard married a woman named Joan, whom the novel portays as a bitter, controlling witch.
1564– Will Shakespeare born, third of 8 children. His father started out as a local glover, who quickly rose through the ranks of local government to become the mayor of the town. They owned a house in Henley street, which also doubled as the glove workshop. For more informaition on this fascinating building, visit the Shakespeare Birthplace trust: https://www.shakespeare.org.uk/visit/shakespeares-birthplace/
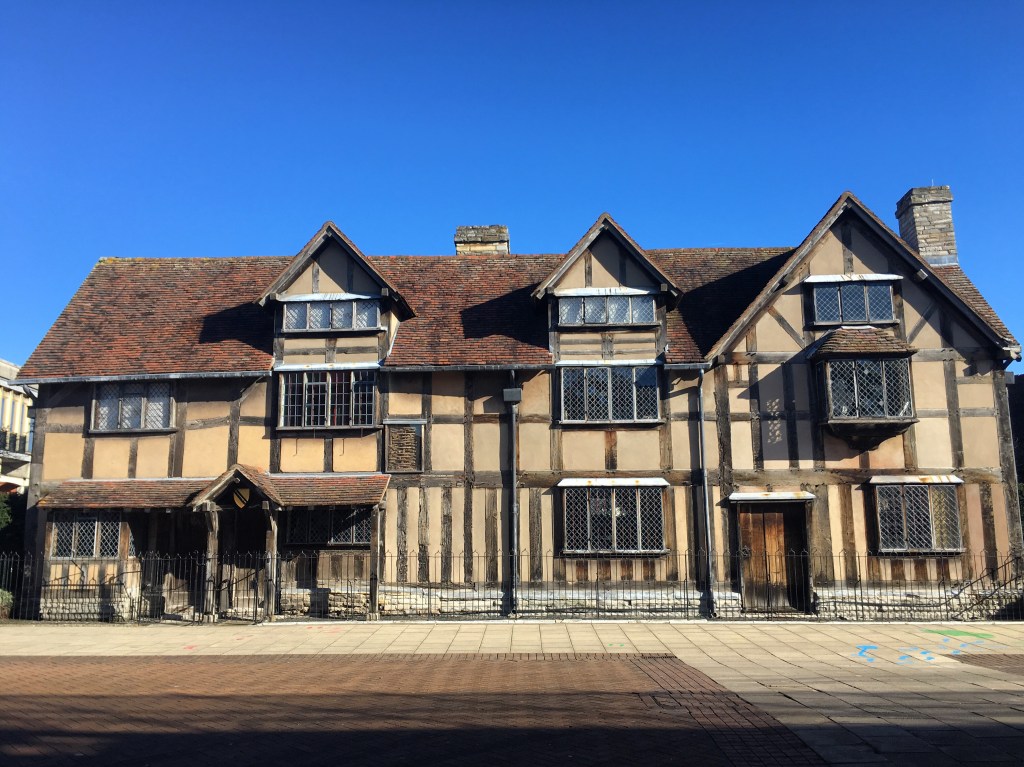


1581– Anne’s father Richard dies, bequeathing her “£6 13s 4d ‘atte the day of her maryage’.” Richard Hathaway owned a farmhouse in Shottery that still stands today! For more info, please visit the Shakespeare Birthplace Trust: https://www.shakespeare.org.uk/visit/shakespeares-birthplace/


1582– On November 27th, 1582, William married Anne Hathaway. He was 18, she was 26. It must have been a hasty and stressful situation. Shakespeare had no job, and based on the timeline, Anne was already pregnant with their daughter Susanna. For more information on marriage in the period, please visit my website on Elizabethan society:
The Shakespeares were granted a marriage licence by the Bishop of Worcester. They were married at Temple Grafton, a village approximately five miles (8 km) from Stratford.
Notes On Shakespeare’s Wedding Day:
- We know that Anne’s family paid a dowry to Shakespeare’s family, which annoys Shakespeare in the book. He feels furious that his father uses the marriage to help his business interests.
- According to Michael Wood, the priest left out the reading of the banns, and suspected the marriage was intentionally catholic. The book also makes it clear that this was a catholic ceremony, deep into the reign of the Protestant Queen Elizabeth I.

May 26, 1583– Susanna Shakespeare is baptized, which means she was probably born three days earlier.
February 2nd, 1585– Hamnet and Judith are baptized.The twins were named after two very close friends of William and Anne, the baker Hamnet Sadler and his wife, Judith. The Sadlers became the godparents of the twins and, in 1589, they in turn named their own son William.
1586– John Shakespeare is booted off the Stratford board of Aldermen for not attending meetings. Michael Wood suggests that John might have been avoiding the meetings because he was in debt, and the creditors knew where to find him. The novel seems to agree with this theory- the first time that we meet John Shakespeare, he is on the verge of beating his own grandson for sneaking up on him. If he was hiding from his creditors, he’d have a reason to be jumpy.
1592 – Shakespeare makes it in London?
1593 Outbreak of Bubonic Plague- 15,000 people died in London alone. O Farrell does a great job of portraying the visceral terror people must have felt during an outbreak, the same terrified panic that gripped our world in 2020. As I’ve written before, not only did the disease itself instill fear, but also the Draconian measures of quarantines, and the grotesque and ineffective methods for treating the plague. To see how you might be treated for plague in the 1590s, take my quiz: https://sites.google.com/d/1iLSGjbllxU-ZwyrUya_xHtjojSCg9pd6/p/1xzNm37sGbHsQJgsnx4irZHJVp9YscVVJ/edit?authuser=2
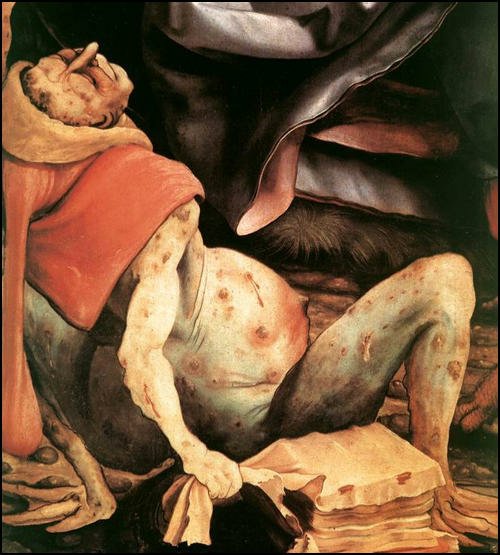
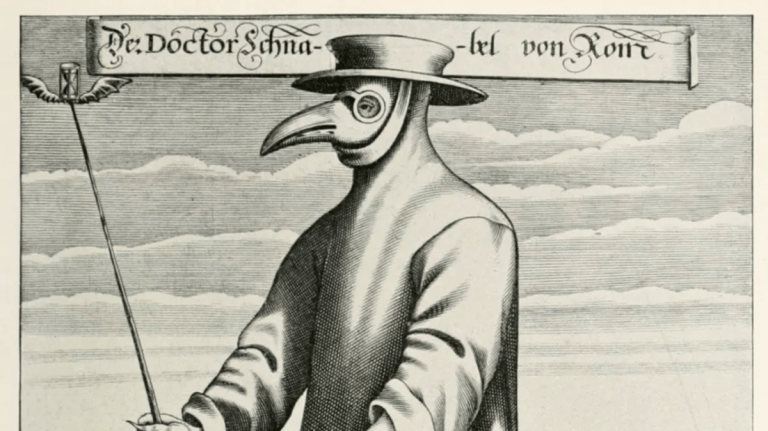



Because of the contagious nature of the disease, the theatres were closed, which forced Shakespeare to write poems instead of plays. Around this time he also probably wrote Romeo and Juliet, Richard III, and A Midsummer Night’s Dream.
Shakespeare published Venus and Adonis
1596 Hamnet dies
C. 1599– William Shakespeare writes Hamlet, his longest play, widely regarded as the greatest play ever written in the English language.

I hope this post helped increase your understanding and enjoyment of the book, and Elizabethan History in general.
For a fascinating look at the life of an Elizabethan woman, check out this documentary about Shakespeare’s mother Mary Arden, created by scholar Michael Wood: