A Midsummer Night’s Dream over Zoom from Ukraine




HAPPY MOTHER’S DAY!
Ever wonder what it was like to be a woman and a mother in Tudor Times? Watch this excellent documentary by Michael Wood










Since Easter and Passover are coming up, (and we are already in the middle of Rhamadan), I thought I’d examine Shakespeare’s depiction of other worlds both celestial and infernal. As the quote above says, philosophers and poets often wonder what greets us in the hereafter, so let me be your guide through Shakespeare’s poetic renderings of heaven and he’ll, accompanied by some gorgeous artwork from HC Selous, William Blake, and others.
Shakespeare was no doubt interested in religion. He quotes from and alludes to the Bible many times in his plays. More importantly, he lived in a time when the national religion changed three times in just 4 years! When Henry VIII changed England to a protestant country, the religious identity of England completely changed:
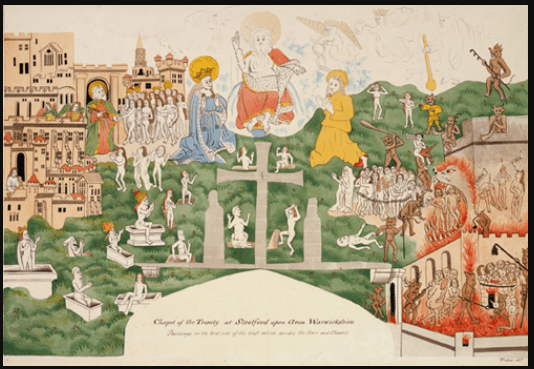
This change was not just felt in monasteries, but in all English churches. King Henry decreed that certain Catholic traditions like Purgatory, indulgences, and praying to saints were idolatrous, and were therefore banned in the Church of England. So, when Shakespeare’s father was called to destroy the “idolatrous” images of the Last Judgement in the Guild Chapel of Stratford’s Holy Trinity Church, he had no choice but to comply. If you click on the link below, you can see a detailed description of the images that Shakespeare no doubt knew well in his family’s church, until his father was forced to literally whitewash them.
Like the images on the Stratford Guild chapel, the ideas of Catholic England didn’t disappear, they were merely hidden from view. Shakespeare refers to these Catholic ideas many times in his plays, especially in Hamlet, a play where a young scholar, who goes to the same school as Martin Luther, is wrestling with the idea of whether the ghost he has seen is a real ghost from purgatory, or a demon from hell, (as protestant churches preached in Shakespeare’s life).

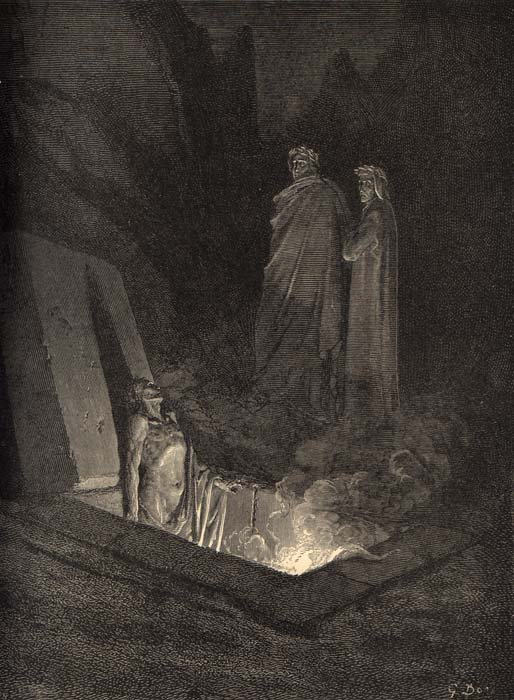
I’ve written before that the ghost of Hamlet’s father teases us with the possibility that he might be a soul in purgatory, the Catholic afterlife realm for those not evil enough for Hell, nor good enough for Heaven. At the height of their powers, monks and bishops sold prayers called indulgences that supposedly allowed a soul’s loved ones to buy them time out of purgatory, thus making them able to ascend to Heaven quicker. The image above is an illustration from Purgatorio, part of Dante’s Divine Comedy, where he visits the soul of
Buonconte da Montefeltro, who is languishing because he doesn’t yet have the strength to get out of purgatory and enter Heaven.
Of course, the Tudor monarchs Henry VIII and Elizabeth I abolished indulgences and proclaimed that purgatory itself didn’t exist, but ideas can’t die, and I feel that Shakespeare was at least inspired by the notion of purgatory, even if he didn’t believe in it himself.

(Horatio) Hamlet, Act I, Scene i.
As a young boy, William Shakespeare was entertained by medieval Mystery plays; amateur theater pieces performed by local artisans that dramatized great stories from the Bible. We know this because he refers to many of the characters in these mystery plays in his own work, especially the villains. King Herod is mentioned in Hamlet and many other plays in and many of Shakespeare’s villains seem to be inspired by the biblical Lucifer, as portrayed in Medieval Mystery Plays.
In this short video of the Yorkshire Mystery play “The Rise and Fall of Lucifer,” we see God (voiced by Sir Patrick Stewart), creating Lucifer as a beautiful angel, who then, dissatisfied with his place in God’s kingdom, is transformed into an ugly devil. At first, Lucifer mourns losing his place in Paradise, but then finds comfort by becomming God’s great antagonist.
Compare this character arc with Shakespeare’s Richard of Gloucester, who also blames his unhappiness on God, (since he feels his disability and deformity are a result of God’s curse). Richard is angry with God, nature, and society, so he wages against them all to become king.
“Then since the heavens hath shaped my body so, let Hell make crook’d my mind to answer it.”
Richard of Gloucester, Henry VI, Part III, Act III, Scene i.
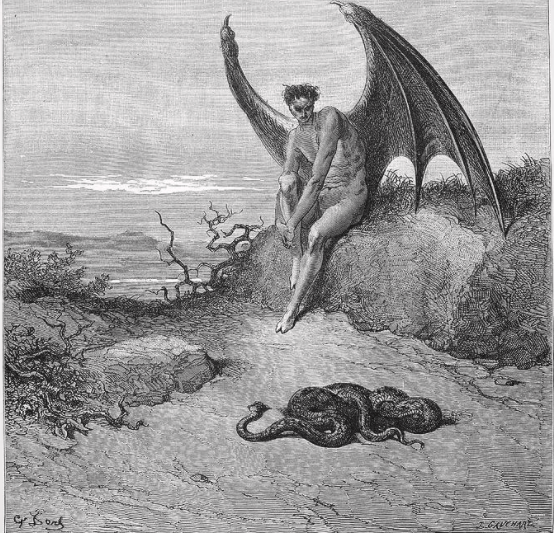


“All is not lost, the unconquerable will, and study of revenge, immortal hate, and the courage never to submit or yield.”
Lucifer― John Milton, Paradise Lost
Claudio. Ay, but to die, and go we know not where;
To lie in cold obstruction and to rot;
This sensible warm motion to become
A kneaded clod; and the delighted spirit
To bathe in fiery floods, or to reside
In thrilling region of thick-ribbed ice;
To be imprison’d in the viewless winds,
And blown with restless violence round about
The pendent world; or to be worse than worst
Of those that lawless and incertain thought Imagine howling: ’tis too horrible!
—Measure For Measure, Act III, Scene i

“Methought I crossed the meloncholy flood with that grim ferryman the poets write of, into the kingdom of perpetual night.”
— Richard III, Act I, Scene iv.

The heavens themselves, the planets and this centre
Observe degree, priority and place,
Insisture, course, proportion, season, form,
Office and custom, in all line of order;
And therefore is the glorious planet Sol
In noble eminence enthroned and sphered
Amidst the other; whose medicinable eye
Corrects the ill aspects of planets evil,
And posts, like the commandment of a king,
Sans cheque to good and bad: but when the planets
In evil mixture to disorder wander,
What plagues and what portents! what mutiny!
What raging of the sea! shaking of earth! Commotion in the winds! frights, changes, horrors,
Divert and crack, rend and deracinate
The unity and married calm of states
Quite from their fixure! O, when degree is shaked,
Which is the ladder to all high designs,
Then enterprise is sick! - Troilus and Cressida, Act I, Scene iii.
https://folgerpedia.folger.edu/Idolatry:_Icons_and_Iconoclasm

I just got approved by Outschool.com to teach a multi-week course on Shakespeare’s comedies!
Get $10 off my class “Shakespeare’s Comic Plays” with coupon code HTHESEJEL310 until May 1, 2022. Get started at https://outschool.com/classes/shakespeares-comic-plays-868BR5hg and enter the coupon code at checkout.






However, the Romans gave way before the good fortune of the man and accepted the bit, and regarding the monarchy as a respite from the evils of the civil wars, they appointed him dictator for life. This was confessedly a tyranny, since the monarchy, besides the element of irresponsibility, now took on that of permanence


Under these circumstances the multitude turned their thoughts towards Marcus Brutus, who was thought to be a descendant of the elder Brutus on his father’s side, on his mother’s side belonged to the Servilii, another illustrious house, and was a son-in‑law and nephew of Cato. 2 The desires which Brutus felt to attempt of his own accord the abolition of the monarchy were blunted by the favours and honours that he had received from Caesar. 3 For not only had his life been spared at Pharsalus after Pompey’s flight, and the lives of many of his friends at his entreaty, but also he had great credit with Caesar. 4 He had received the most honourable of the praetorships for the current year, and was to be consul three years later, having been preferred to Cassius, who was a rival candidate. 5 For Caesar, as we are told, said that Cassius urged the juster claims to the office, but that for his own part he could not pass Brutus by.105 6 Once, too, when certain persons were actually accusing Brutus to him, the conspiracy being already on foot, Caesar would not heed them, but laying his hand upon his body said to the accusers: “Brutus will wait for this shrivelled skin,”106 implying that Brutus was worthy to rule because of his virtue, but that for the sake of ruling he would not become a thankless villain. 7 Those, however, who p589 were eager for the change, and fixed their eyes on Brutus alone, or on him first, did not venture to talk with him directly, but by night they covered his praetorial tribune and chair with writings, most of which were of this sort: “Thou art asleep, Brutus,” or, “Thou art not Brutus.”107 8 When Cassius perceived that the ambition of Brutus was somewhat stirred by these things, he was more urgent with him than before, and pricked him on, having himself also some private grounds for hating Caesar;

So far, perhaps, these things may have happened of their own accord; the place, however, which was the scene of that struggle and murder, and in which the senate was then assembled, since it contained a statue of Pompey and had been dedicated by Pompey as an additional ornament to his p597 theatre, made it wholly clear that it was the work of some heavenly power which was calling and guiding the action thither.

Well, then, Antony, who was a friend of Caesar’s and a robust man, was detained outside by Brutus Albinus,110 who purposely engaged him in a lengthy conversation; 5 but Caesar went in, and the senate rose in his honour. Some of the partisans of Brutus took their places round the back of Caesar’s chair, while others went to meet him, as though they would support the petition which Tulliusº Cimber presented to Caesar in behalf of his exiled brother, and they joined their entreaties to his and accompanied Caesar up to his chair. 6 But when, after taking his seat, Caesar continued to repulse their petitions, and, as they pressed upon him with greater importunity, began to show anger towards one and another of them, Tullius seized his toga with both hands and pulled it down from his neck. This was the signal for the assault. 7 It was Casca who gave him the first blow with his dagger, in the neck, not a mortal wound, nor even a deep one, for which he was too much confused, as was natural at the beginning of a deed of great daring; so that Caesar turned about, grasped the knife, and held it fast. p599 8 At almost the same instant both cried out, the smitten man in Latin: “Accursed Casca, what does thou?” and the smiter, in Greek, to his brother: “Brother, help!”

9 So the affair began, and those who were not privy to the plot were filled with consternation and horror at what was going on; they dared not fly, nor go to Caesar’s help, nay, nor even utter a word. 10 But those who had prepared themselves for the murder bared each of them his dagger, and Caesar, hemmed in on all sides, whichever way he turned confronting blows of weapons aimed at his face and eyes, driven hither and thither like a wild beast, was entangled in the hands of all; 11 for all had to take part in the sacrifice and taste of the slaughter. Therefore Brutus also gave him one blow in the groin. 12 And it is said by some writers that although Caesar defended himself against the rest and darted this way and that and cried aloud, when he saw that Brutus had drawn his dagger, he pulled his toga down over his head and sank, either by chance or because pushed there by his murderers, against the pedestal on which the statue of Pompey stood. 13
And the pedestal was drenched with his blood, so that one might have thought that Pompey himself was presiding over this vengeance upon his enemy, who now lay prostrate at his feet, quivering from a multitude of wounds. 14 For it is said that he received twenty-three; and many of the conspirators were wounded by one another, as they struggled to plant all those blows in one body.
-Plutarch’s Life Of Caesar









James Shapiro in his book 1599, addresses the common complaint that in the play that bears his name, Julius Caesar dies halfway through the play and has little time onstage to make a connection with the audience. The play is about tyrananicide, what causes it, what it looks like, and especially its aftermath. In a time when Jesuits and Catholic radicals threatened to assassinate Queen Elizabeth, Shakespeare wrote a powerful story about how fragile government systems can be; how striking the head off Rome leads to anarchy and sometimes tyranny.

Ave and Happy Pie Day ! Since it’s Roman month, I thought I’d talk about the most infamous pie in Shakespeare’s Roman plays, and give you an ancient Roman recipe that tastes a lot better!
In Act V of Titus Andronicus, the titular general and his household cook and serve the Empress’ sons to their mother in a pie! Here’s how the scene plays out in the 1999 film Titus:
Before he cooks the Empress’ sons, Titus actually tells them what he is going to do to them, like some kind of psychotic chef giving a cooking program:
This one hand yet is left to cut your throats,
Whilst that Lavinia 'tween her stumps doth hold
The basin that receives your guilty blood.
You know your mother means to feast with me,
And calls herself Revenge, and thinks me mad:
Hark, villains! I will grind your bones to dust
And with your blood and it I'll make a paste,
And of the paste a coffin I will rear
And make two pasties of your shameful heads,
And bid that strumpet, your unhallow'd dam,
Like to the earth swallow her own increase.
This is the feast that I have bid her to,
And this the banquet she shall surfeit on;
I’ve adapted Titus’ recipe into this creepy recipe card below:

Now when Titus says coffin he’s actually referring to a pie crust, (though ironically this coffin will also be a tomb for two human bodies). Ancient Romans did in fact make meat pies, so Tamara wouldn’t have immediately been suspicious It also was not unheard of for the ancient Romans to actually eat brains! According to DE RE COQUINARIA, one of the oldest surviving Roman cookbooks, there was a recipe called Patina frisilis, a pudding made of fresh vegetables, wine, and calf brains:
Take vegetables, clean and wash, shred and cook them cool them off and drain them. Take 4 calf’s brains, remove the skin and strings and cook them4 in the mortar put 6 scruples of pepper, moisten with broth and crush fine; then add the brains, rub again and meanwhile add the vegetables, rubbing all the while, and make a fine paste of it. Thereupon break and add 8 eggs. Now add a glassful of broth, a glassful of wine, a glassful of raisin wine, taste this preparation. Oil the baking dish thoroughly put the mixture in the dish and place it in the hot plate, (that is above the hot ashes) and when it is done unmould it sprinkle with pepper and serve.
APICIUS- DE RE COQUINARIA (c. 1st century CE).

My research suggests that the coffin was mainly just flour and oil and was not actually intended to be eaten. It would be similar to a modern salt crust pie that seals in juices and helps preserve the pie in the absence of refrigerators.
Thankfully Apicius has another recipe for a Roman pie that I find much more appetizing
A dish of elderberries, either hot or cold, is made in this manner: take elderberries, wash them; cook in water, skim and strain. Prepare a dish in which to cook the custard; crush 6 scruples of pepper with a little broth; add this to the elderberry pulp with another glass of broth, a glass of wine, a glass of raisin wine and as much as 4 ounces of oil. Put the dish in the hot bath and stir the contents. As soon as it is getting warm, quickly break 6 eggs and whipping them, incorporate them, in order to thicken the fluid. When thick enough sprinkle with pepper and serve up.
While I’m at it, here’s another historical pie recipe that was a favorite of Shakespeare’s Richard II:
I apologize for not spending enough time on black history month this February.
If I do prove her haggard,
Though that her jesses were my dear heartstrings,
I’ld whistle her off and let her down the wind,
To pray at fortune. Haply, for I am black
Or for I am declined
Into the vale of years,—yet that’s not much—
She’s gone. I am abused; and my relief
Must be to loathe her.
Othello, Act III, Scene iii.
Psychologists say some men expect the worst of everyone, especially women. I would argue that Othello is an example of a man who has been threatened so often, he expects the worst of everyone, especially his wife, and this is why it’s so easy for Iago to manipulate him.
I don’t know what it’s like to be black in 21st century America let alone the trauma of Othello’s life, which was riddled with hardship such as being sold into Slavery, encountering Cannibals, and rising through the ranks of an army that doesn’t quite trust him. But based on the psychology of people who undergo trauma, the text of the play, and some details about Venetian life, I think looking at Othello through the perspective of trauma and toxic masculinity is an illuminating interpretation of the play.
I want to be clear that I am not saying domestic violence is condonable, or that being black has anything to do with abuse. What I am trying to say is that Othello is a play that in my view sheds a light on trauma, PTSD, toxic masculinity, and systemic oppression.
In the book Beyond Anger, psychologist Thomas J. Harbin illustrates just how easily a man can deceive himself with jealousy brought on by his own insecurities.
Angry men often believe that others do not approve of them, or think highly of them so more than likely when you assume you know what another is thinking you will assume that person is thinking negative thoughts about you more garbage yen when you For example and whenever [Othello] notices that his wife is not in a good mood, he asks “What’s wrong with you?” his wife usually says that nothing is wrong but [Othello] assumes that she is not telling the truth, and that she is actually angry with him. He then gets angry because he assumes she is blaming him for something that he didn’t do; the ‘garbage out’ mind reading is also frustrating to those around you friends coworkers and family can see that you are getting angry with them, but they have no idea why.
J. Thomas Harbin, “Beyond Anger,” 2018.
Actor Adrian Lester doesn’t think that the play is about race, but about the trauma of military society and according to Aryanna Thompson of George Washington University, he hoped the audience would see Othello as a soldier, not a black man, when he played the role at the National Theater in 2003, when England and America were engaged in military interventions in Iraq.
Though this interpretation works, I would argue that the exploitation of people of color is very much what the play is about, not just on stage but also in places like the military. “The play’s military context is short-lived, serving mainly as a framework for the intense private wars that follow. And in this emotional arena, Othello is far less secure.” Maybe Othello’s toxic insecurities come from being seen as disposable by the Venetian upper crust. Like Shylock before him, Othello is an alien in his own country and if he offends anyone, he will be crushed. He is then put in a dangerous situation where the troops have to hurry up and wait for the danger to find them, which is always a recipe for disaster as the clip above shows.
Maybe a lot of black people felt this feeling of cultural disposibility in the 1600s: listen to professor Thompson talk about the way black people were exploited in the Elizabethan and Jacobean era:
If you watched this clip, you might notice that for most of the history of the play, the draw has been seeing white actors ‘rise to the challenge’ of playing a black man. Sadly, Othello the character is not only exploited by characters in his own play, the role has been exploited as a novelty by theater companies for centuries. My point here is that I see merit to the question of whether or not this play deserves to be performed since from the beginning, it was designed to exploit blackness and the stereotypes of blackness by white actors.
Trauma makes abuse understandable but it doesn’t make it right. The cycle must be broken. Shakespeare’s gift here is to show how toxic masculinity is ultimately self destructive. Plus racial oppression and sexual repression leads everyone into tragedy.
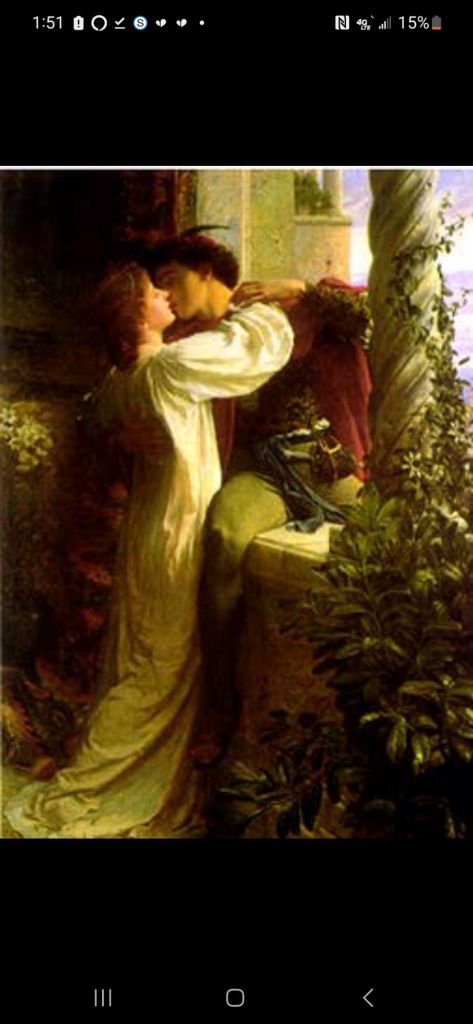





I’ve seen four live productions of Romeo and Juliet, (5 if you include West Side Story). I’ve also watched four films (6 if you include West Side Story and Gnomio and Juliet) and one thing that I’ve noticed again and again, and again is that you can tell the whole story of the play with clothing. This is a story about families who are part of opposite factions whose children secretly meet, marry, die, and fuse the families into one, and their clothes can show each step of that journey.
The feud
Nearly every story about a conflict or war uses contrasting colors to show the different factions. Sometimes even real wars become famous for the clothes of the opposing armies. The Revolutionary War between the redcoats and the blue and gold Continentals, the American Civil War between the Rebel Grays and the Yankee Bluebellies. In almost every production I’ve ever seen, the feud in Romeo and Juliet is also demonstrated by the opposing factions wearing distinctive clothing.

Historically, warring factions in Itally during the period the original Romeo and Juliet is set, wore distinctive clothes and banners as well. . In this medieval drawing, you can see Italians in the Ghibelline faction, who were loyal to the Holy Roman Empire, fighting the Guelph faction (red cross), who supported the Pope. Powerful families were constantly fighting and taking sides in the Guelf vs. ghibelines conflict in Verona, which might have inspired the Capulet Montegue feud in Romeo and Juliet.
Even the servants of the nobles got roped into these conflicts, and they literally wore their loyalties on their sleeves. The servants wore a kind of uniform or livery to show what household they belonged to. The servants Gregory and Sampson owe their jobs to Lord Capulet, and are willing to fight to protect his honor. Perhaps Shakespeare started the play with these servants to make this distinction very obvious. Here’s a short overview on Italian Liveries from the Metropolitan Museum of Art:
https://www.metmuseum.org/art/collection/search/86582
In 1966, director Franco Zepherelli set a trend with his iconic use of color in his movie. He chose to make the Capulets wear warm tones while the Montegues wore blue and silver. Juliet (Olivia Hussey) wore a gorgeous red dress that made her look youthful, passionate, and lovely, while Tybalt (Michael York), wore red, orange, and black to emphasize his anger, and jealousy (which has been associated for centuries with the color orange). By contrast, the Montagues like Romeo (Leonard Whiting) wore blue, making him look peaceful and cool. These color choices not only clearly indicate who belongs to which contrasting factions, but also help telegraph the character’s personalities. Look at the way these costumes make the two lovers stand out even when they’re surrounded by people at the Capulet ball:

Zepherilli’s color choices were most blatantly exploited in the kids film Gnomio and Juliet, where they did away with the names Capulet and Montegue altogether, and just called the two groups of gnomes the Reds and the Blues.
The Dance
To get Romeo and Juliet to meet and fall in love, Shakespeare gives them a dance scene for them to meet and fall in love. He further makes it clear that when they first meet, Romeo is in disguise. The original source Shakespeare used made the dance a carnival ball, (which even today is celebrated in Italy with masks). Most productions today have Romeo wearing a mask or some other costume so that he is not easily recognizable as a Montague. Masks are a big part of Italian culture, especially in Venice during Carnival:
In the 1996 movie, Baz Luhrman creates a bacchanal costume party, where nobody wears masks but the costumes help telegraph important character points. Mercutio is dressed in drag, which not only displays his vibrant personality but also conveniently distracts everyone from the fact that Romeo is at the Capulet party with no mask on.
Capulet is dressed like a Roman emperor, which emphasizes his role as the patriarch of the Capulet family. Juliet (Claire Danes) is dressed as an angel, to emphasize the celestial imagery Shakespeare uses to describe her. Finally, Romeo (Leonardo DiCaprio) is dressed as a crusader knight because of the dialogue in the play when he first meets Juliet:
Romeo. [To JULIET] If I profane with my unworthiest hand
This holy shrine, the gentle fine is this:720
My lips, two blushing pilgrims, ready stand
To smooth that rough touch with a tender kiss.
Juliet. Good pilgrim, you do wrong your hand too much,
Which mannerly devotion shows in this;
For saints have hands that pilgrims' hands do touch,725
And palm to palm is holy palmers' kiss.
Romeo. Have not saints lips, and holy palmers too?
Juliet. Ay, pilgrim, lips that they must use in prayer.
Romeo. O, then, dear saint, let lips do what hands do;
They pray, grant thou, lest faith turn to despair.730
Juliet. Saints do not move, though grant for prayers' sake.
Romeo. Then move not, while my prayer's effect I take.
Thus from my lips, by yours, my sin is purged.
Juliet. Then have my lips the sin that they have took.
Romeo. Sin from thy lips? O trespass sweetly urged!735
Give me my sin again.
Juliet. You kiss by the book. Romeo and Juliet, Act I, Scene V, Lines 719-737.
Notice that Romeo calls Juliet a saint, and later an angel in the famous balcony scene, which explains her costume at the ball. Juliet refers to Romoe as a Pilgrim, which is a cheeky comment on his crusader knight costume. In the Crusades, crusader knights made pilgrimages to the holy land, with the hope that God (and presumably, his angels) would forgive their sins. Romeo’s name even means “Pilgrim.” Luhrman makes clever nods to Shakespeare’s text by dressing Romeo and Juliet in this way, and gives the dialogue a bit of a playful roleplay as the characters make jokes about each other’s costumes- Romeo hopes that he will go on a pilgrimage and that this angel will take his sin with a kiss.
In Gnomio and Juliet, the titular characters meet in a different kind of disguise. Rather than going to a dance with their family, they are both simultaneously trying to sneak into a garden and steal a flower, so they are both wearing black, ninja-inspired outfits. Their black clothing helps them meet and interact without fear of retribution from their parents (since they do not yet know that they are supposed to be enemies. The ninja clothes also establishes that for these two gnomes, love of adventure unites them. Alas though, it doesn’t last; Juliet finds out that Gnomio is a Blue, when they both accidentally fall in a pool, stripping their warpaint off and revealing who they are.
Sometimes the dance shows a fundamental difference between the lovers and the feuding factions. West Side Story is a 20th-century musical that re-imagines the feuding families as juvenile street gangs, who like their Veronese counterparts, wear contrasting colors. The Jets (who represent the Montagues) wear Blue and yellow, while the Sharks (Capulets), wear red and black. The gang members continue wearing these colors on the night of the high school dance, except for Tony and Maria (the Romeo and Juliet analogs). In most productions I’ve seen, (including the 2021 movie), these young lovers wear white throughout the majority of the play, to emphasize the purity of their feelings, and their rejection of violence. Thus, unlike Shakespeare’s version of the story, West Side Story makes the lovers unquestionably purer are more peaceful than Shakespeare’s Romeo and Juliet, and their clothing makes this clear.

The Merging of the family
(8:30-11:00)
Costume Designer Charlene in the 2006 AU production deliberately had the characters change clothes when they get married. Juliet was wearing the same iconic red dress as Olivia Hussey for the first two acts of the play but then changed into a pale blue gown that matches Romeo. The clothes re-enforce the idea that the marriage represents Romeo and Juliet abandoning their family’s conflicts, and simply showing their true colors.


Another way of getting everyone in the family to subconsciously unite in grief would be to costume everyone wearing black except Romeo and Juliet. At the end of the play, The Capulets are already mourning Juliet, (because she faked her death in Act IV), and the Montegues are already mourning Lady Montegue (who died offstage). Just by these circumstances, everyone could come onstage wearing black, uniting in their grief, which is further solidified when they see their children dead onstage.
Not all productions choose to costume the characters like warring factions, but nevertheless, any theatrical production’s costumes must telegraph something about the characters. In these production slides for a production I worked on in 2012, the costumes reflect the distinct personality of each character and show a class difference between the Montagues and the Capulets.
The 2013 Film: Costumes Done Badly
The 2013 movie is more concerned with showing off the beauty of the actor’s faces, and the literal jewels than the clothes:
Most of the actors and costumes are literally in the dark for most of the film, probably because the film was financed by the Swarofski Crystal company, who literally wanted the film to sparkle. Ultimately, like most jewelry, I thought the film was pretty to look at, but the costumes and cinematography had little utilitarian value. The costumes and visual didn’t tell the story efficiently, but mainly was designed to distract the audience with the beauty of the sets, costumes and the attractive young actors. The only thing I liked was a subtle choice to make Juliet’s mask reminiscent of Medusa, the monster in Greek Myth, who could turn people to stone with a look. I liked that the film was subtly implying that love, at first sight, can be lethal.