Month: February 2022
Rotten state of Hamlet analysis | William Shakespeare | The Guardian
https://www.theguardian.com/culture/2022/feb/13/rotten-state-of-hamlet-analysis
What do you think? Is she right and Hamlet is a simple play that’s been made complicated by time, or is there something deeper that she’s misses.
New Podcast: Romeo and Juliet, Act I, Scene v
I’ve published a dramatic reading with a wonderful actress, Sara Hricik, of Act I, Scene v of “Romeo and Juliet.” This is the scene where Romeo meets Juliet for the first time at the Capulet’s ball. Notice how in this scene, they actually form a perfect 14 line sonnet:
Romeo. [To JULIET] If I profane with my unworthiest hand This holy shrine, the gentle fine is this:720 My lips, two blushing pilgrims, ready stand To smooth that rough touch with a tender kiss. Juliet. Good pilgrim, you do wrong your hand too much, Which mannerly devotion shows in this; For saints have hands that pilgrims' hands do touch,725 And palm to palm is holy palmers' kiss. Romeo. Have not saints lips, and holy palmers too? Juliet. Ay, pilgrim, lips that they must use in prayer. Romeo. O, then, dear saint, let lips do what hands do; They pray, grant thou, lest faith turn to despair.730 Juliet. Saints do not move, though grant for prayers' sake. Romeo. Then move not, while my prayer's effect I take. Thus from my lips, by yours, my sin is purged. Juliet. Then have my lips the sin that they have took. Romeo. Sin from thy lips? O trespass sweetly urged!735 Give me my sin again. Juliet. You kiss by the book.
If you liked this reading, and want to know more about this sceen and "Romeo and Juliet" as a whole, please sign up for my Romeo and Juliet classes. I have an intro class that covers the plot and character, and a more immersive class, where you learn how Shakespeare's company rehearsed and inhabited these characters!
Happy Valentines Day 💝! Enjoy some Shakespearean Candy Hearts 💕




New Podcast: My Favorite Sonnets
My Favorite Sonnets
Since Valentines Day is next week, I thought I’d talk a little bit about Shakespeare’s love poems. Every year I try to study a sonnet or two and write one of my own for my wife and my family. So here’s some insight into the sonnets and I hope that this inspires you to read and craft your own love poems.
What Is A Sonnet?
Shakespeare wrote 154 short poems called sonnets.
They are 14 lines long
Each line has 10 syllables, generally in iambic pentameter
12 of the 14 lines are grouped into 3 groups of 4 lines called quatrains
The final two lines are called a rhyming couplet

A little History
The first collection of Shakespeare’s Sonnets was published in 1609, but NOT BY SHAKESPEARE.
We don’t know if this is the order he intended, we don’t know if he intended them to be published, and we DEFINITELY DON”T KNOW IF THEY ARE AUTOBIOGRAPHICAL.
Themes and Ideas
A lot of the sonnets use extended metaphors where the speaker describes his feelings by describing himself as another person, place, or thing. In some sonnets, he’s a painter or looking in a mirror, or an astronomer looking through a telescope or outdoors in nature and something reminds him of the beloved. Most follow a similar theme:
You’re beautiful like… [or] I’m trying to write about you but…
You wil age and die.
TIme and the sonnets


The most pervasive idea in the sonnet is a fight against Time. Time is often personified in the sonnets as being jealous, cruel, cold, unfeeling or petty. Time is also associated with the concept of Death. Like the Grim Reaper, he is the enemy of romantic love because he makes young lovers age and die.
Devouring Time, blunt thou the lion’s paws,
And make the earth devour her own sweet brood;
Sonnet 19
THe BIG BUT..
In most of the sonnets there’s a “But” around the third quatrain (lines 9-12 or thereabouts), which challenges the power of time or Death. For example, the first 8 sonnets basically say: “You will age BUT… you will become immortal if you have children.”
Couplet
The Young Man sonnets (1-126)
From fairest creatures we desire increase,
That thereby beauty’s rose might never die,
But as the riper should by time decease,
His tender heir might bear his memory:
William Shakespeare, Sonnet 1

The first 126 sonnets (roughly) are about a young man with blonde hair. Though there is no evidence that the sonnets were autobiographical, many scholars have speculated that he might have been partially inspired by Henry Wriosley, the Earl of Southampton. Shakespeare dedicated two poems to Henry: The Rape of Lucrece and Venus and Adonis, which you can see the title page of here:

Sonnet 12
When I do count the clock that tells the time,
And see the brave day sunk in hideous night;
When I behold the violet past prime,
And sable curls, all silvered o’er with white;
When lofty trees I see barren of leaves,
Which erst from heat did canopy the herd,
And summer’s green all girded up in sheaves,
Borne on the bier with white and bristly beard,
Then of thy beauty do I question make,
That thou among the wastes of time must go,
Since sweets and beauties do themselves forsake
And die as fast as they see others grow;
And nothing ‘gainst Time’s scythe can make defense
Save breed, to brave him when he takes thee hence
I love this sonnet for its use of alliteration, the use of words that sound the same: “count,” “clock” “tells,” “time,” “green,” “girdled,” etc. The use of “count,” and “clock” in particular makes you imagine the sound of a clock in your head. The sonnet makes you keenly aware of the passage of time, first from the seconds of a ticking clock, then to the changing of the seasons, then at last to the span of a lifetime. This sonnet might not inspire much in terms of feelings, but its technical construction literally works ‘like clockwork.’ If you’re interested in r Elizabethan clocks and other timekeeping instruments, click here for a fascinating blog: https://www.cassidycash.com/did-shakespeare-have-a-clock-part-1-of-5/
Sonnet 18
Shall I compare thee to a summer's day? Thou art more lovely and more temperate: Rough winds do shake the darling buds of May, And summer's lease hath all too short a date: Sometime too hot the eye of heaven shines, And often is his gold complexion dimmed, And every fair from fair sometime declines, By chance, or nature's changing course untrimmed: But thy eternal summer shall not fade, Nor lose possession of that fair thou ow'st, Nor shall death brag thou wander'st in his shade, When in eternal lines to time thou grow'st, So long as men can breathe, or eyes can see, So long lives this, and this gives life to thee.
I go into detail explaining sonnet 18 in my class: “Love Poetry Shakespeare Style,” but to put it succinctly, this sonnet is famous for talking about the ways the beloved is Better than a summer’s day.
Sonnet 27- “Weary With Toil…
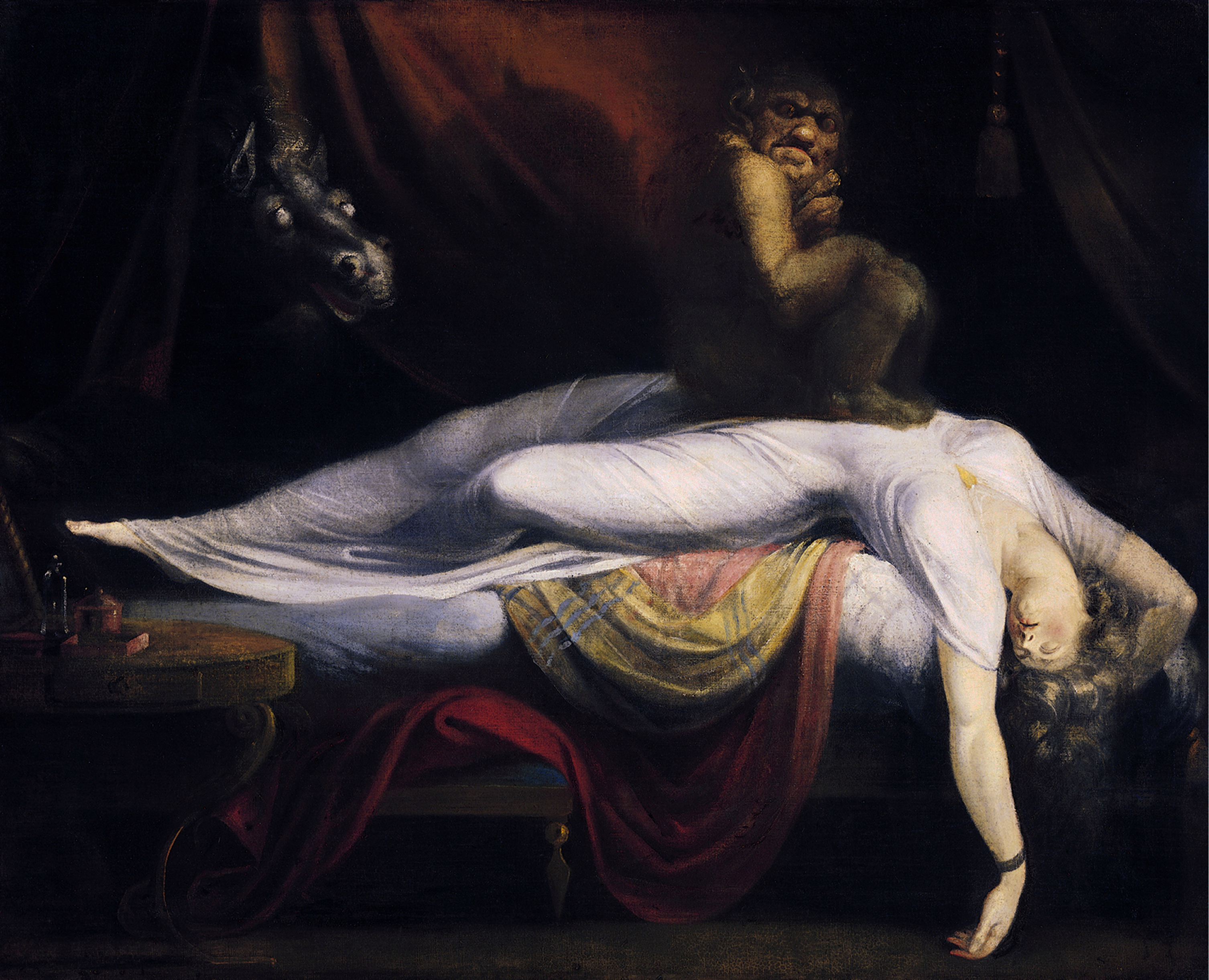


Weary with toil, I haste me to my bed, The dear repose for limbs with travel tired; But then begins a journey in my head To work my mind, when body's work's expired: For then my thoughts--from far where I abide-- Intend a zealous pilgrimage to thee, And keep my drooping eyelids open wide, Looking on darkness which the blind do see: Save that my soul's imaginary sight Presents thy shadow to my sightless view, Which, like a jewel hung in ghastly night, Makes black night beauteous, and her old face new. Lo! thus, by day my limbs, by night my mind, For thee, and for myself, no quiet find.
Not to seem crass, but this sonnet is literally panting with sexual desire. The speaker is exhausted but cannot sleep, with the image of his beloved haunting his thoughts. There are also a few religious allusions too where the speaker calls himself a “pilgrim,” much like Romeo and Juliet in their first meeting in Act I, Scene v. It almost seems like the beloved is both an angel that the speaker wants to bless him, and a succubus or vampire draining him of love and life.
XXIX “When In disgrace…”
Sonnet 29: “When in disgrace With Fortune and men’s eyes
When in disgrace with fortune and men's eyes I all alone beweep my outcast state, And trouble deaf heaven with my bootless cries, And look upon myself, and curse my fate, Wishing me like to one more rich in hope, Featured like him, like him with friends possessed, Desiring this man's art, and that man's scope, With what I most enjoy contented least; Yet in these thoughts my self almost despising, Haply I think on thee, and then my state, Like to the lark at break of day arising From sullen earth, sings hymns at heaven's gate; For thy sweet love remembered such wealth brings That then I scorn to change my state with kings.
Sonnet 118- The “Marriage” Sonnet

Let me not to the marriage of true minds admit impediments.
– Shakespeare, Sonnet 29
Let me not to the marriage of true minds
Admit impediments. Love is not love
Which alters when it alteration finds,
Or bends with the remover to remove:
O, no! it is an ever-fixed mark,
That looks on tempests and is never shaken;
It is the star to every wandering bark,
Whose worth's unknown, although his height be taken.
Love's not Time's fool, though rosy lips and cheeks
Within his bending sickle's compass come;
Love alters not with his brief hours and weeks,
But bears it out even to the edge of doom.
If this be error and upon me proved,
I never writ, nor no man ever loved.
This sonnet is one of the most famous poems in all of English literature all. In fact, it's quite personally important to me, because my wife recited it to me on my wedding day. It is full of powerful metaphors about how married love is stronger and more resilent than simple lust or infatuation. On my wedding day it was a powerful affirmation that my wife and I will endure age, change, Time, and eventually death, but our love will remain the same.
The Dark Lady Sonnets 127-152
Sonnets 127-152 seem to be collectively addressed to a woman with dark hair, dark skin, and musical talent, who seems to be in a love triangle with the speaker of the sonnets, and someone else. As you can see in this video, many theories have come up to try and expose who she really was, but again, he have no proof that these sonnets were in any way autobiographical.
As far as we know, the Dark Lady sonnets might simply have been a writing exercise for Shakespeare while he was writing Othello and Antony and Cleopatra. I’m not interested in the Dark Lady conspiracy, except for its usefulness for historians to highlight important Elizabethan women. I have to admit that I wouldn’t have known about Emilia Lanier, or the Countess of Pembroke if they hadn’t been roped into the Dark Lady theory. Otherwise, I’m only interested in the Dark Lady sonnets for their poetry and the interesting stories they tell.
In the old age black was not counted fair, Or if it were, it bore not beauty's name; But now is black beauty's successive heir, And beauty slandered with a bastard shame: For since each hand hath put on Nature's power, Fairing the foul with Art's false borrowed face, Sweet beauty hath no name, no holy bower, But is profaned, if not lives in disgrace. Therefore my mistress' eyes are raven black, Her eyes so suited, and they mourners seem At such who, not born fair, no beauty lack, Sland'ring creation with a false esteem: Yet so they mourn becoming of their woe, That every tongue says beauty should look so.
I admit this is a retroactive reading, but Shakespeare has been guilty of equating fair skin with beauty, so it’s nice to see this sonnet, which lends itself to a refutation of that notion. Much like how “Hath not a Jew eyes…” has been appropriated as a plea for tolerance, I hope this sonnet gains popularity as a source of pride for POC.
In the old age black was not counted fair,
Or if it were, it bore not beauty’s name;
But now is black beauty’s successive heir,
And beauty slandered with a bastard shame:
For since each hand hath put on Nature’s power,
Fairing the foul with Art’s false borrowed face,
Sweet beauty hath no name, no holy bower,
But is profaned, if not lives in disgrace.
Therefore my mistress’ eyes are raven black,
Her eyes so suited, and they mourners seem
At such who, not born fair, no beauty lack,
Sland’ring creation with a false esteem:
Yet so they mourn becoming of their woe,
That every tongue says beauty should look so.
Sonnet 128
How oft when thou, my music, music play’st,
Upon that blessed wood whose motion sounds
With thy sweet fingers when thou gently sway’st
The wiry concord that mine ear confounds,
Do I envy those jacks that nimble leap,
To kiss the tender inward of thy hand,
Whilst my poor lips which should that harvest reap,
At the wood’s boldness by thee blushing stand!
To be so tickled, they would change their state
And situation with those dancing chips,
O’er whom thy fingers walk with gentle gait,
Making dead wood more bless’d than living lips.
Since saucy jacks so happy are in this,
Give them thy fingers, me thy lips to kiss.
Sonnet 130
My mistress’ eyes are nothing like the sun;
Coral is far more red, than her lips red:
If snow be white, why then her breasts are dun;
If hairs be wires, black wires grow on her head.
I have seen roses damasked, red and white,
But no such roses see I in her cheeks;
And in some perfumes is there more delight
Than in the breath that from my mistress reeks.
I love to hear her speak, yet well I know
That music hath a far more pleasing sound:
I grant I never saw a goddess go,
My mistress, when she walks, treads on the ground:
And yet by heaven, I think my love as rare,
As any she belied with false compare.
I ended with this sonnet, because unlike the previous ones, Shakespeare beautifully shows the frankness and honesty in true love. Shakespeare doesn’t use extravagant praise or pretty metaphors, but instead just says he loves his mistress for who she is. I wish that all of you reading this will find a love that you can enjoy without false comparison, (but then again, what is life without a little poetry in it)?
Happy Valentine’s Day!
Did Shakespeare Celebrate Valentines?

You probably know that I love to speculate and do a little historical detective work and find out whether Elizabethans like Shakespeare celebrated our modern holidays and then compare and contrast how they celebrated them back then versus how we do today. Valentine’s Day is a day we associate with love and poetry, so of course, I wondered if the most celebrated poet of the Renaissance celebrated it himself!
Based on my findings, if Shakespeare celebrated Valentine’s Day, he probably did mainly what we did- writing letters and poems to his beloved and maybe sending a trinket of love. It’s unlikely he celebrated it like modern Catholics do to honor the martyrdom of a Catholic saint. In my research, I was surprised to learn that Valentine’s Day has been celebrated for hundreds of years and has its roots in a holiday that Shakespeare describes in one of his most famous plays.
Part I: The Feast of Lupercal: Valentine’s Day’s Dark Ancestor
According to NPR’s podcast: “The Dark Origins of Valentine’s Day”, like Christmas, Halloween, and many other holidays, the Christian holiday of St. Valentine’s day was designed to replace the pagan holiday of Lupercal, which was a Roman fertility festival where men engaged in basically what we’d now call- swingers’ parties or key parties where they’d draw a woman’s name from a lottery and… couple for the night.
https://www.npr.org/2011/02/14/133693152/the-dark-origins-of-valentines-day
The Lupercal was also synonymous with the founding of Rome. Lupa is the name of the wolf that saved the infants Romulus and Remus, who would become the first kings of Rome. If you click here, you can read an article about a recent archeological discovery; a cave found under Rome that was once revered as the place where Romulus and Remus lived with Lupa:
https://follyfancier.wordpress.com/2007/11/20/lupercal-grotto-found-under-rome/
Shakespeare actually starts his play of Julius Caesar on the Lupercal, and makes reference to its status as a fertility festival. In Act I, Caesar is watching Antony run a race and tells him to be sure to touch Calpurnia, owing to the superstition that if a man touches a barren woman on Lupercal, it will make her capable of bearing children:
Caesar. Calpurnia!
Calpurnia. Here, my lord. 85
Caesar. Stand you directly in Antonius' way,
When he doth run his course. Antonius!
Antony. Caesar, my lord?
Caesar. Forget not, in your speed, Antonius,
To touch Calpurnia; for our elders say, 90
The barren, touched in this holy chase,
Shake off their sterile curse.
Antony. I shall remember:
When Caesar says 'do this,' it is perform'd.
Caesar. Set on; and leave no ceremony out. Julius Caesar, Act I, Scene ii, Lines 84-95
Shakespeare leaves out that, according to tradition, Antony should be naked and anointed with goat’s blood and slap Calpurnia with a goatskin thong, but that was part of the Roman Lupercal festival.

Part II: The Beginnings of St. Valentine’s Day
https://www.history.com/news/real-st-valentine-medieval
St. Valentine was either a Catholic priest or bishop who was martyred in the 3rd century AD (Source History.com). According to tradition, he conducted Christian marriages in defiance of Roman law, and rejected the concept of Lupercalian coupling, which is why Emperor Claudius murdered him. Thus, the holiday is intentionally meant to replace Lupercalia, and celebrate monogamous relationships under the Christian God. The popular story is that before his death, he sent a letter to the young daughter of a family he converted to Christianity and signed it: “Your Valentine,” thus starting the tradition of signing cards in this manner. In the 5th century, Pope Gelasius made Valentine’s day an official Catholic feast day to replace Lupercal once and for all.
Part III: The oldest surviving Valentines
Evidence is sketchy on how the traditions of Valentine’s Day evolved, in the Middle Ages, but in Catholic Europe, the concept of celebrating married love on Valentine’s Day spread, and poets like Chaucer and Shakespeare helped popularize it.
Geoffrey Chaucer wrote in the 14th century of how birds would choose their mates on Valentine’s Day:
For this was sent on Seynt Valentyne's day
Whan every foul cometh ther to choose his mate.
According to History.com, there’s a possibility that Chaucer invented the idea of a St. Valentine’s feast, and forever linked it with the celebration of love:
The medieval English poet Geoffrey Chaucer often took liberties with history, placing his poetic characters into fictitious historical contexts that he represented as real. No record exists of romantic celebrations on Valentine’s Day prior to a poem Chaucer wrote around 1375. In his work “Parliament of Foules,” he links a tradition of courtly love with the celebration of St. Valentine’s feast day–an association that didn’t exist until after his poem received widespread attention. The poem refers to February 14 as the day birds (and humans) come together to find a mate.
Hanes, Elizabeth. “Six Surprising Facts about Valentines Day.” https://www.history.com/news/6-surprising-facts-about-st-valentine
This theme has been repeated in other pieces of literature. In John Lydgate’s 15th-century poem, “A Valentine to Her that Excelleth All”, he writes of how it was the custom on Valentine’s Day for people to choose their love:
To look and search Cupid’s Calendar and choose their choose by great affection.
John Ludgate: “”A Valentine to her that Excelleth All”
The Paston’s oldest surviving valentines
In the 1470s in a series of correspondence, from Margery Brews to her husband John Paston refers to the latter as “My right well-beloved Valentine, John Paston, Esquire.”
Margery also wrote adoring letters to John, who was probably away frequently, fighting in the Hundred Years War, and advising Margary’s kinsman, John Fastolfe, (whom Shakespeare mentions in Henry VI, Part I. Her poetry is very tender and must have comforted her husband much:
And if ye command me to keep me true wherever I go,
I wis I will de all my might you to love, and never no mo(re).
And if my friends say, that I do amiss,
They shall not me let so for to do,
Mine heart me bids ever more to love you
Truly over all earthly thing,
And if they be never so wrath
I trust it shall be better in time coming.
Margery’s letters are some of the earliest surviving Valentine’s poetry. Her letters prove that the tradition of giving poetry to one’s beloved during February was around in the 15th century, and probably while Shakespeare was a child in the 16th.
Shakespeare’s contributions to Valentine’s Day
Shakespeare mentions Saint Valentine’s Day twice in his works. In A Midsummer Night’s Dream, (a play that is set in Ancient Greece and has connections to Lupercal), he builds on Chaucer’s claim that Valentine’s Day is the day that birds couple for the night. Duke Theseus and Aegeus discover the four lovers asleep. They are surprised that they are sharing the same ground, since Lysander and Demetrius (as far as the old men know), are rivals for Hermia’s affection.
Egeus. My lord, this is my daughter here asleep;
And this, Lysander; this Demetrius is;
This Helena, old Nedar’s Helena:1685
I wonder of their being here together.
Theseus. No doubt they rose up early to observe
The rite of May, and hearing our intent,
Came here in grace our solemnity.
But speak, Egeus; is not this the day1690
That Hermia should give answer of her choice?
Egeus. It is, my lord.
Theseus. Go, bid the huntsmen wake them with their horns.
[Horns and shout within. LYSANDER, DEMETRIUS,]
HELENA, and HERMIA wake and start up]1695
Good morrow, friends. Saint Valentine is past:
Begin these wood-birds but to couple now?
Shakespeare has a much darker reference to Valentine’s Day in Hamlet:
Ophelia has gone mad with the loss of her brother, her father, and Hamlet breaking her heart. She starts wandering the castle and can only communicate through songs. She sings a very melancholy song that alludes to the superstition that if two single people meet on the morning of Saint Valentine’s Day they will likely get married:
Tomorrow is Saint Valentine’s Day,
All in the morning betime,
And I a maid at your window,
To be your Valentine.
Then up he rose
And donned his clothes
And dupped the chamber door
Let in a maid then out a maid
Never departed more.
Ophelia seems to be darkly admitting that she and Hamlet have had pre-marital intimate relations and she is no longer a virgin, The song implies that Ophelia entered Hamlet’s chamber a maid (that is, an unmarried virgin), but is let out a maid (unmarried), while the Hamlet very clearly has taken her virginity. Hamlet re-enforces this suspicion by commanding her to go to a nunnery, one of the only recourse for single mothers. It is reasonable to assume that Shakespeare is implying that Ophelia is in fact pregnant, and is driven mad with sorrow that she now has to deliver her baby without any form of support from her father (who is dead), from her brother (who is in France), or her baby’s father, who wants her to leave and never return. Ophelia’s song is a lament that she wishes the superstition were true, and Hamlet had indeed married her.
It’s unlikely that Shakespeare celebrated Valentine’s Day as a religious holiday, after all, Queen Elizabeth had made England a Protestant country. Celebrating a saint day could have been seen as idolatrous in Protestant England. Nevertheless, Shakespeare and other romantic writers helped transform Valentine’s Day into less of a religious holiday, and more as a secular celebration of love and monogamy, very different from its bloody, promiscuous roots.
Sources:
- Paston Letters
- https://www.npr.org/2011/02/14/133693152/the-dark-origins-of-valentines-day
- https://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/entry/Valentine%27s_Day#Customs_around_the_world
- https://www.tudorsociety.com/14-february-valentines-day/
- https://www.theanneboleynfiles.com/valentines-day-in-tudor-england/